| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Forces are given many names, such as push, pull, thrust, lift, weight, friction, and tension. Traditionally, forces have been grouped into several categories and given names relating to their source, how they are transmitted, or their effects. The most important of these categories are discussed in this section, together with some interesting applications. Further examples of forces are discussed later in this text.
Weight (also called force of gravity) is a pervasive force that acts at all times and must be counteracted to keep an object from falling. You definitely notice that you must support the weight of a heavy object by pushing up on it when you hold it stationary, as illustrated in [link] (a). But how do inanimate objects like a table support the weight of a mass placed on them, such as shown in [link] (b)? When the bag of dog food is placed on the table, the table actually sags slightly under the load. This would be noticeable if the load were placed on a card table, but even rigid objects deform when a force is applied to them. Unless the object is deformed beyond its limit, it will exert a restoring force much like a deformed spring (or trampoline or diving board). The greater the deformation, the greater the restoring force. So when the load is placed on the table, the table sags until the restoring force becomes as large as the weight of the load. At this point the net external force on the load is zero. That is the situation when the load is stationary on the table. The table sags quickly, and the sag is slight so we do not notice it. But it is similar to the sagging of a trampoline when you climb onto it.
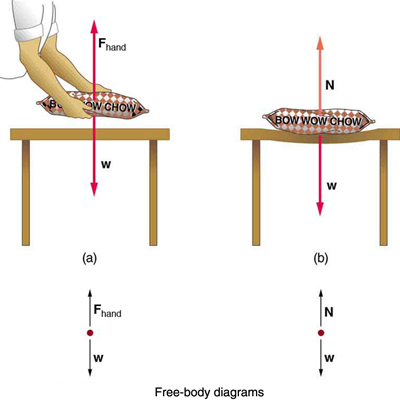
We must conclude that whatever supports a load, be it animate or not, must supply an upward force equal to the weight of the load, as we assumed in a few of the previous examples. If the force supporting a load is perpendicular to the surface of contact between the load and its support, this force is defined to be a normal force and here is given the symbol . (This is not the unit for force N.) The word normal means perpendicular to a surface. The normal force can be less than the object’s weight if the object is on an incline, as you will see in the next example.
In this section we have introduced the quantity normal force, which is represented by the variable . This should not be confused with the symbol for the newton, which is also represented by the letter N. These symbols are particularly important to distinguish because the units of a normal force ( ) happen to be newtons (N). For example, the normal force that the floor exerts on a chair might be . One important difference is that normal force is a vector, while the newton is simply a unit. Be careful not to confuse these letters in your calculations! You will encounter more similarities among variables and units as you proceed in physics. Another example of this is the quantity work ( ) and the unit watts (W).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?