| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
To obtain an equation for Newton’s second law, we first write the relationship of acceleration and net external force as the proportionality
where the symbol means “proportional to,” and is the net external force . (The net external force is the vector sum of all external forces and can be determined graphically, using the head-to-tail method, or analytically, using components. The techniques are the same as for the addition of other vectors, and are covered in Two-Dimensional Kinematics .) This proportionality states what we have said in words— acceleration is directly proportional to the net external force . Once the system of interest is chosen, it is important to identify the external forces and ignore the internal ones. It is a tremendous simplification not to have to consider the numerous internal forces acting between objects within the system, such as muscular forces within the child’s body, let alone the myriad of forces between atoms in the objects, but by doing so, we can easily solve some very complex problems with only minimal error due to our simplification
Now, it also seems reasonable that acceleration should be inversely proportional to the mass of the system. In other words, the larger the mass (the inertia), the smaller the acceleration produced by a given force. And indeed, as illustrated in [link] , the same net external force applied to a car produces a much smaller acceleration than when applied to a basketball. The proportionality is written as
where is the mass of the system. Experiments have shown that acceleration is exactly inversely proportional to mass, just as it is exactly linearly proportional to the net external force.
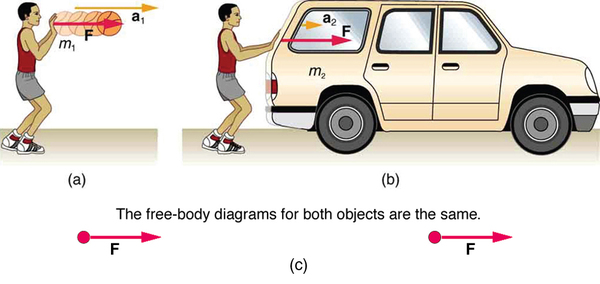
It has been found that the acceleration of an object depends only on the net external force and the mass of the object. Combining the two proportionalities just given yields Newton's second law of motion.
The acceleration of a system is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net external force acting on the system, and inversely proportional to its mass.
In equation form, Newton’s second law of motion is
This is often written in the more familiar form
When only the magnitude of force and acceleration are considered, this equation is simply
Although these last two equations are really the same, the first gives more insight into what Newton’s second law means. The law is a cause and effect relationship among three quantities that is not simply based on their definitions. The validity of the second law is completely based on experimental verification.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?