| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Superconductors are materials with a resistivity of zero. They are familiar to the general public because of their practical applications and have been mentioned at a number of points in the text. Because the resistance of a piece of superconductor is zero, there are no heat losses for currents through them; they are used in magnets needing high currents, such as in MRI machines, and could cut energy losses in power transmission. But most superconductors must be cooled to temperatures only a few kelvin above absolute zero, a costly procedure limiting their practical applications. In the past decade, tremendous advances have been made in producing materials that become superconductors at relatively high temperatures. There is hope that room temperature superconductors may someday be manufactured.
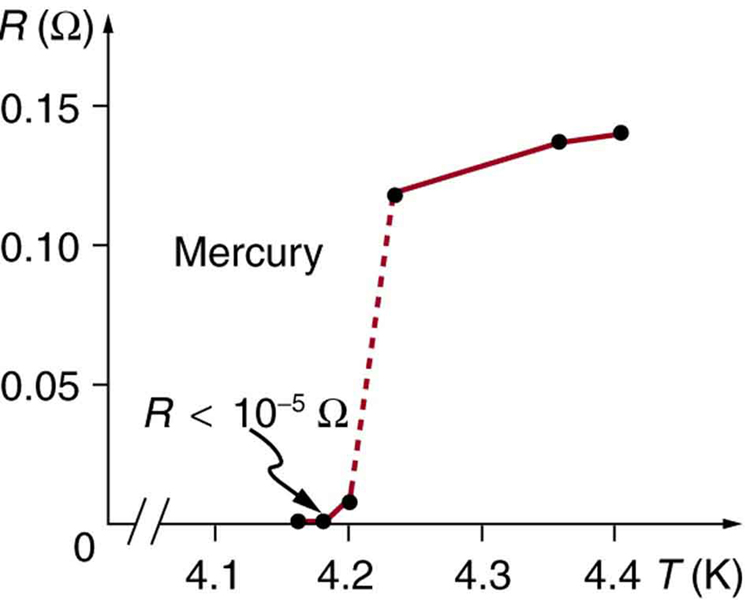
Superconductivity was discovered accidentally in 1911 by the Dutch physicist H. Kamerlingh Onnes (1853–1926) when he used liquid helium to cool mercury. Onnes had been the first person to liquefy helium a few years earlier and was surprised to observe the resistivity of a mediocre conductor like mercury drop to zero at a temperature of 4.2 K. We define the temperature at which and below which a material becomes a superconductor to be its critical temperature , denoted by . (See [link] .) Progress in understanding how and why a material became a superconductor was relatively slow, with the first workable theory coming in 1957. Certain other elements were also found to become superconductors, but all had s less than 10 K, which are expensive to maintain. Although Onnes received a Nobel prize in 1913, it was primarily for his work with liquid helium.
In 1986, a breakthrough was announced—a ceramic compound was found to have an unprecedented of 35 K. It looked as if much higher critical temperatures could be possible, and by early 1988 another ceramic (this of thallium, calcium, barium, copper, and oxygen) had been found to have (see [link] .) The economic potential of perfect conductors saving electric energy is immense for s above 77 K, since that is the temperature of liquid nitrogen. Although liquid helium has a boiling point of 4 K and can be used to make materials superconducting, it costs about $5 per liter. Liquid nitrogen boils at 77 K, but only costs about $0.30 per liter. There was general euphoria at the discovery of these complex ceramic superconductors, but this soon subsided with the sobering difficulty of forming them into usable wires. The first commercial use of a high temperature superconductor is in an electronic filter for cellular phones. High-temperature superconductors are used in experimental apparatus, and they are actively being researched, particularly in thin film applications.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?