| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
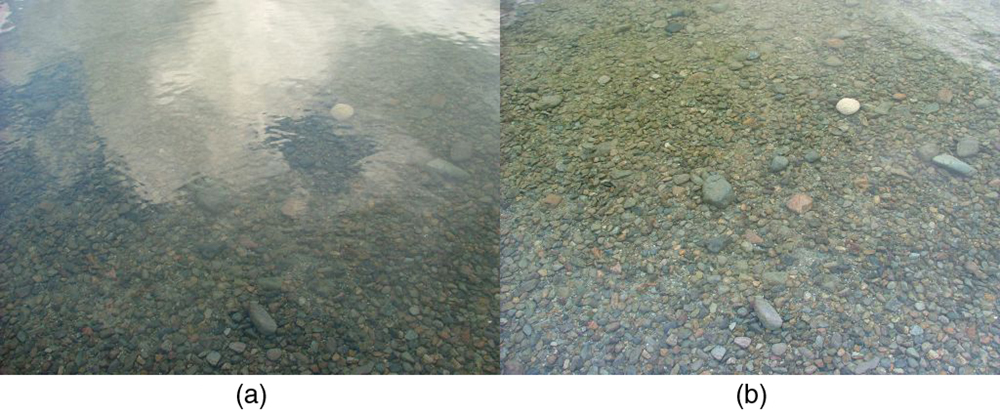
Polaroid sunglasses are familiar to most of us. They have a special ability to cut the glare of light reflected from water or glass (see [link] ). Polaroids have this ability because of a wave characteristic of light called polarization. What is polarization? How is it produced? What are some of its uses? The answers to these questions are related to the wave character of light.

Light is one type of electromagnetic (EM) wave. As noted earlier, EM waves are transverse waves consisting of varying electric and magnetic fields that oscillate perpendicular to the direction of propagation (see [link] ). There are specific directions for the oscillations of the electric and magnetic fields. Polarization is the attribute that a wave’s oscillations have a definite direction relative to the direction of propagation of the wave. (This is not the same type of polarization as that discussed for the separation of charges.) Waves having such a direction are said to be polarized . For an EM wave, we define the direction of polarization to be the direction parallel to the electric field. Thus we can think of the electric field arrows as showing the direction of polarization, as in [link] .
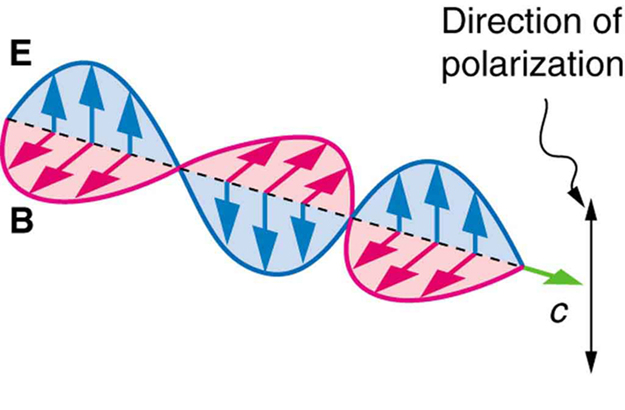
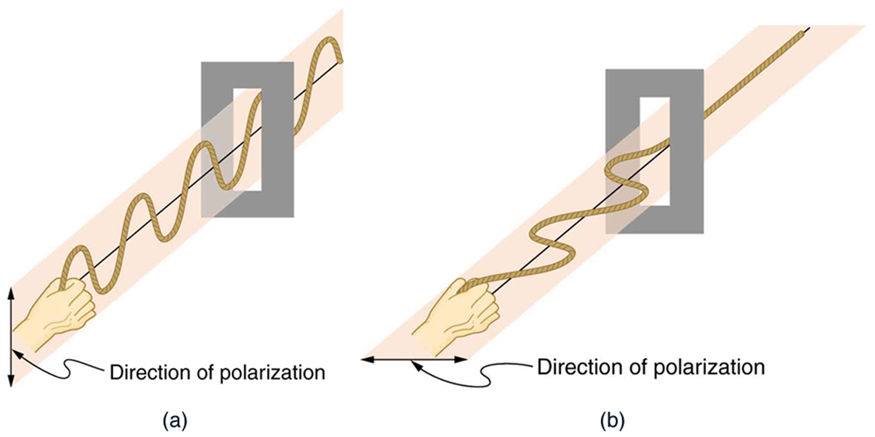
To examine this further, consider the transverse waves in the ropes shown in [link] . The oscillations in one rope are in a vertical plane and are said to be vertically polarized . Those in the other rope are in a horizontal plane and are horizontally polarized . If a vertical slit is placed on the first rope, the waves pass through. However, a vertical slit blocks the horizontally polarized waves. For EM waves, the direction of the electric field is analogous to the disturbances on the ropes.
The Sun and many other light sources produce waves that are randomly polarized (see [link] ). Such light is said to be unpolarized because it is composed of many waves with all possible directions of polarization. Polaroid materials, invented by the founder of Polaroid Corporation, Edwin Land, act as a polarizing slit for light, allowing only polarization in one direction to pass through. Polarizing filters are composed of long molecules aligned in one direction. Thinking of the molecules as many slits, analogous to those for the oscillating ropes, we can understand why only light with a specific polarization can get through. The axis of a polarizing filter is the direction along which the filter passes the electric field of an EM wave (see [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?