| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Although Christiaan Huygens thought that light was a wave, Isaac Newton did not. Newton felt that there were other explanations for color, and for the interference and diffraction effects that were observable at the time. Owing to Newton’s tremendous stature, his view generally prevailed. The fact that Huygens’s principle worked was not considered evidence that was direct enough to prove that light is a wave. The acceptance of the wave character of light came many years later when, in 1801, the English physicist and physician Thomas Young (1773–1829) did his now-classic double slit experiment (see [link] ).
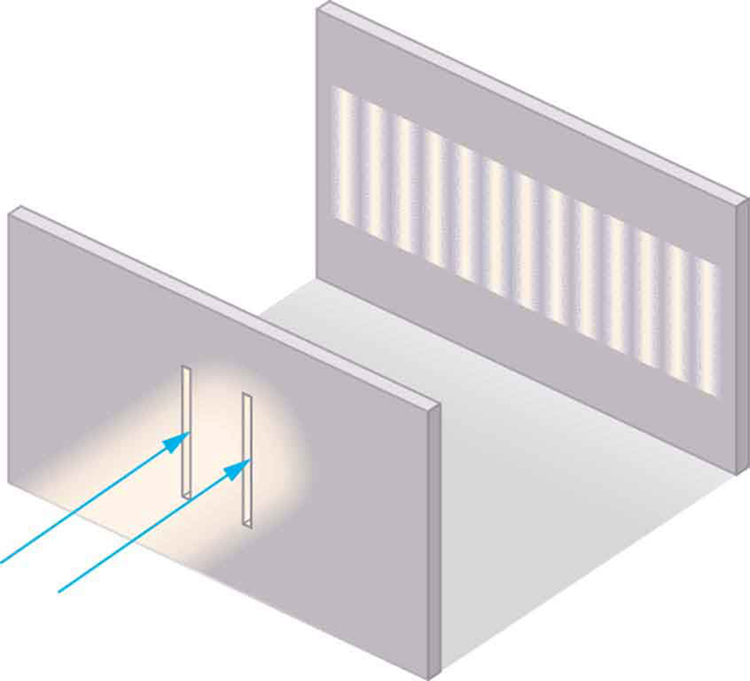
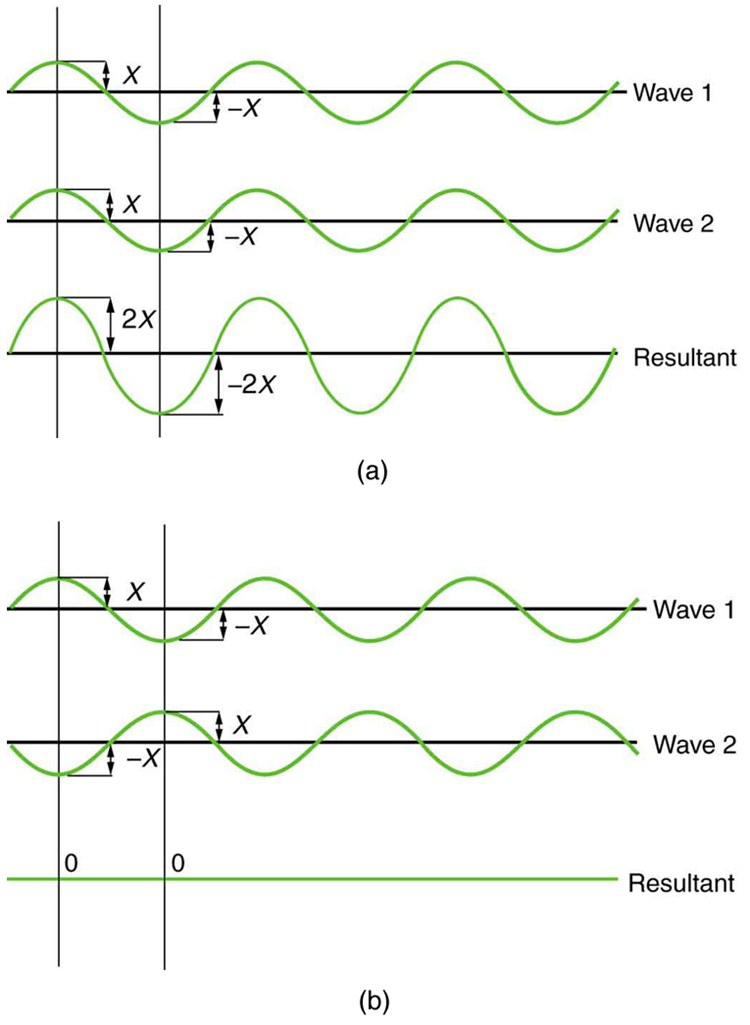
Why do we not ordinarily observe wave behavior for light, such as observed in Young’s double slit experiment? First, light must interact with something small, such as the closely spaced slits used by Young, to show pronounced wave effects. Furthermore, Young first passed light from a single source (the Sun) through a single slit to make the light somewhat coherent. By coherent , we mean waves are in phase or have a definite phase relationship. Incoherent means the waves have random phase relationships. Why did Young then pass the light through a double slit? The answer to this question is that two slits provide two coherent light sources that then interfere constructively or destructively. Young used sunlight, where each wavelength forms its own pattern, making the effect more difficult to see. We illustrate the double slit experiment with monochromatic (single ) light to clarify the effect. [link] shows the pure constructive and destructive interference of two waves having the same wavelength and amplitude.
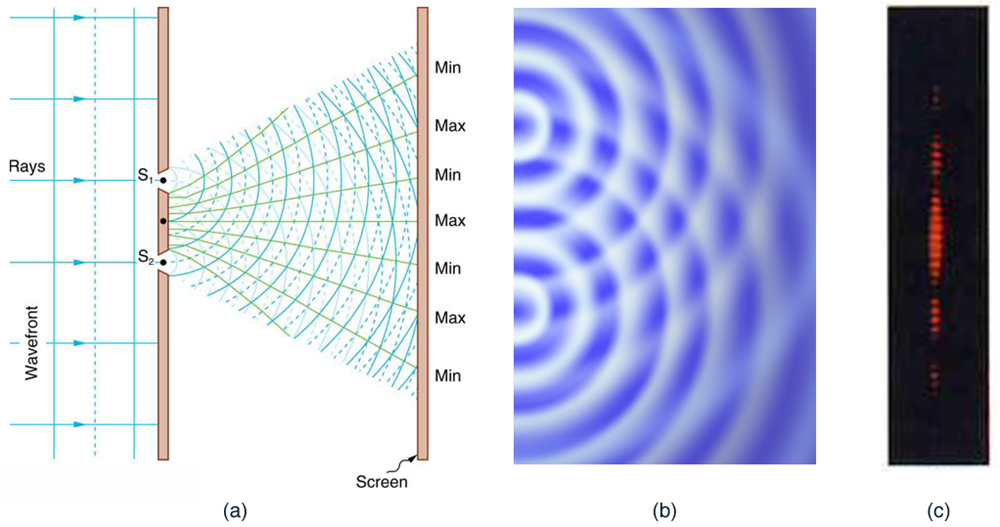
When light passes through narrow slits, it is diffracted into semicircular waves, as shown in [link] (a). Pure constructive interference occurs where the waves are crest to crest or trough to trough. Pure destructive interference occurs where they are crest to trough. The light must fall on a screen and be scattered into our eyes for us to see the pattern. An analogous pattern for water waves is shown in [link] (b). Note that regions of constructive and destructive interference move out from the slits at well-defined angles to the original beam. These angles depend on wavelength and the distance between the slits, as we shall see below.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?