| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Electric generators induce an emf by rotating a coil in a magnetic field, as briefly discussed in Induced Emf and Magnetic Flux . We will now explore generators in more detail. Consider the following example.
The generator coil shown in [link] is rotated through one-fourth of a revolution (from to ) in 15.0 ms. The 200-turn circular coil has a 5.00 cm radius and is in a uniform 1.25 T magnetic field. What is the average emf induced?
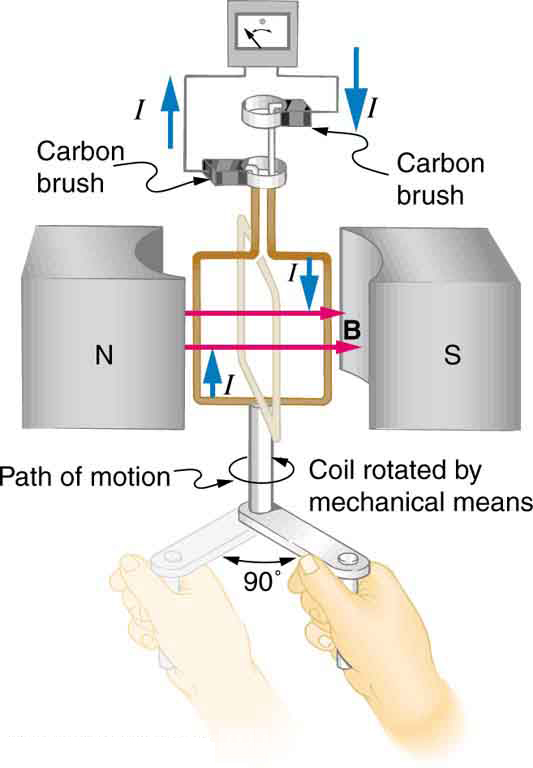
Strategy
We use Faraday’s law of induction to find the average emf induced over a time :
We know that and , and so we must determine the change in flux to find emf.
Solution
Since the area of the loop and the magnetic field strength are constant, we see that
Now, , since it was given that goes from to . Thus , and
The area of the loop is . Entering this value gives
Discussion
This is a practical average value, similar to the 120 V used in household power.
The emf calculated in [link] is the average over one-fourth of a revolution. What is the emf at any given instant? It varies with the angle between the magnetic field and a perpendicular to the coil. We can get an expression for emf as a function of time by considering the motional emf on a rotating rectangular coil of width and height in a uniform magnetic field, as illustrated in [link] .
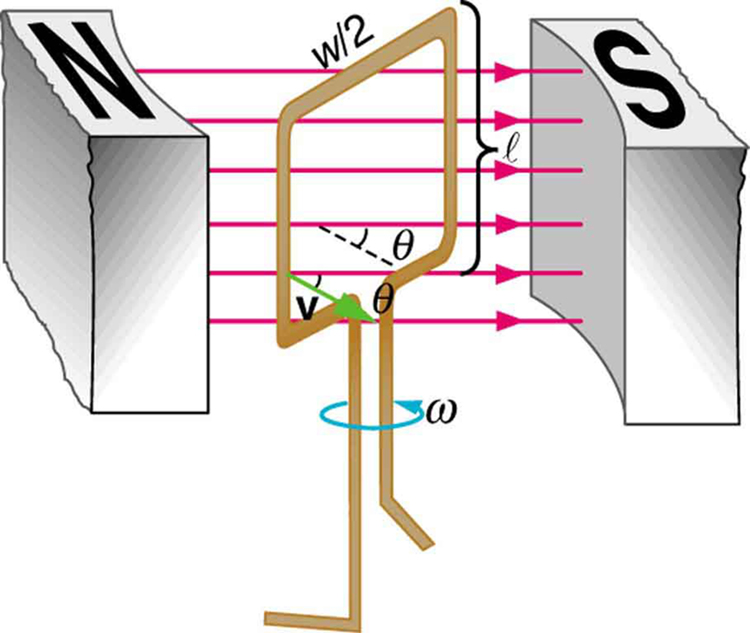
Charges in the wires of the loop experience the magnetic force, because they are moving in a magnetic field. Charges in the vertical wires experience forces parallel to the wire, causing currents. But those in the top and bottom segments feel a force perpendicular to the wire, which does not cause a current. We can thus find the induced emf by considering only the side wires. Motional emf is given to be , where the velocity v is perpendicular to the magnetic field . Here the velocity is at an angle with , so that its component perpendicular to is (see [link] ). Thus in this case the emf induced on each side is , and they are in the same direction. The total emf around the loop is then
This expression is valid, but it does not give emf as a function of time. To find the time dependence of emf, we assume the coil rotates at a constant angular velocity . The angle is related to angular velocity by , so that
Now, linear velocity is related to angular velocity by . Here , so that , and

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?