| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
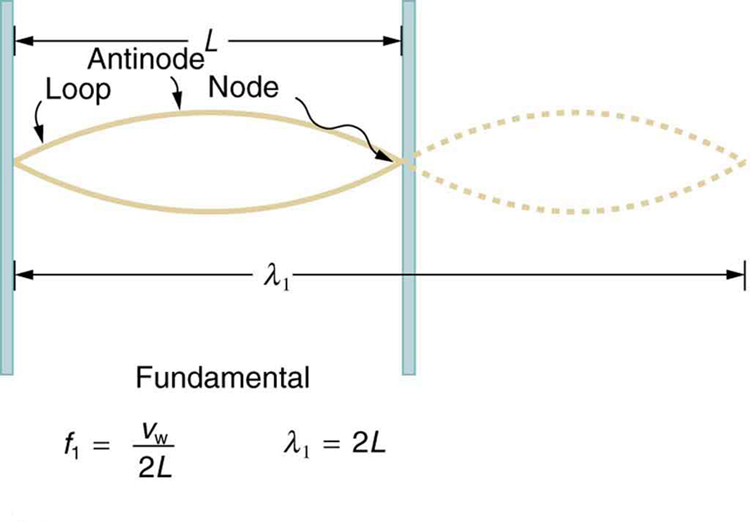
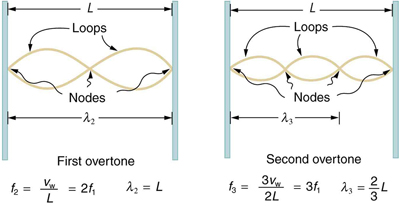
The lowest frequency, called the fundamental frequency , is thus for the longest wavelength, which is seen to be . Therefore, the fundamental frequency is . In this case, the overtones or harmonics are multiples of the fundamental frequency. As seen in [link] , the first harmonic can easily be calculated since . Thus, . Similarly, , and so on. All of these frequencies can be changed by adjusting the tension in the string. The greater the tension, the greater is and the higher the frequencies. This observation is familiar to anyone who has ever observed a string instrument being tuned. We will see in later chapters that standing waves are crucial to many resonance phenomena, such as in sounding boxes on string instruments.
Striking two adjacent keys on a piano produces a warbling combination usually considered to be unpleasant. The superposition of two waves of similar but not identical frequencies is the culprit. Another example is often noticeable in jet aircraft, particularly the two-engine variety, while taxiing. The combined sound of the engines goes up and down in loudness. This varying loudness happens because the sound waves have similar but not identical frequencies. The discordant warbling of the piano and the fluctuating loudness of the jet engine noise are both due to alternately constructive and destructive interference as the two waves go in and out of phase. [link] illustrates this graphically.
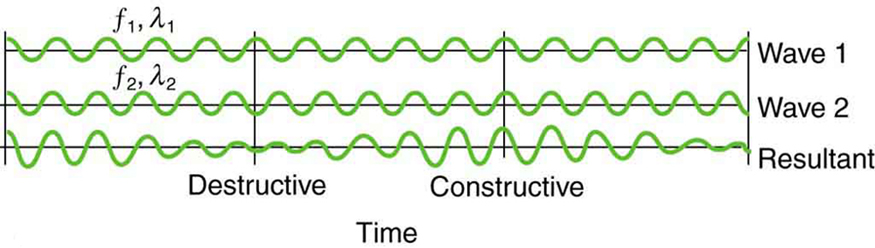
The wave resulting from the superposition of two similar-frequency waves has a frequency that is the average of the two. This wave fluctuates in amplitude, or beats , with a frequency called the beat frequency . We can determine the beat frequency by adding two waves together mathematically. Note that a wave can be represented at one point in space as
where is the frequency of the wave. Adding two waves that have different frequencies but identical amplitudes produces a resultant
More specifically,
Using a trigonometric identity, it can be shown that
where
is the beat frequency, and is the average of and . These results mean that the resultant wave has twice the amplitude and the average frequency of the two superimposed waves, but it also fluctuates in overall amplitude at the beat frequency . The first cosine term in the expression effectively causes the amplitude to go up and down. The second cosine term is the wave with frequency . This result is valid for all types of waves. However, if it is a sound wave, providing the two frequencies are similar, then what we hear is an average frequency that gets louder and softer (or warbles) at the beat frequency.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?