| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Matter most commonly exists as a solid, liquid, or gas; these states are known as the three common phases of matter . Solids have a definite shape and a specific volume, liquids have a definite volume but their shape changes depending on the container in which they are held, and gases have neither a definite shape nor a specific volume as their molecules move to fill the container in which they are held. (See [link] .) Liquids and gases are considered to be fluids because they yield to shearing forces, whereas solids resist them. Note that the extent to which fluids yield to shearing forces (and hence flow easily and quickly) depends on a quantity called the viscosity which is discussed in detail in Viscosity and Laminar Flow; Poiseuille’s Law . We can understand the phases of matter and what constitutes a fluid by considering the forces between atoms that make up matter in the three phases.
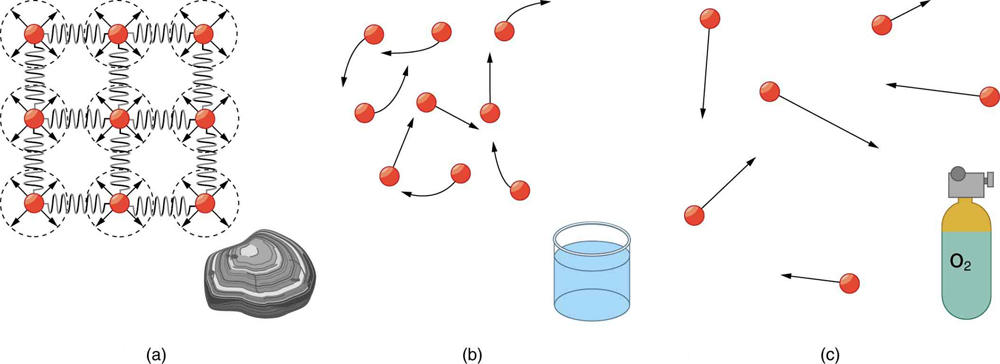
Atoms in solids are in close contact, with forces between them that allow the atoms to vibrate but not to change positions with neighboring atoms. (These forces can be thought of as springs that can be stretched or compressed, but not easily broken.) Thus a solid resists all types of stress. A solid cannot be easily deformed because the atoms that make up the solid are not able to move about freely. Solids also resist compression, because their atoms form part of a lattice structure in which the atoms are a relatively fixed distance apart. Under compression, the atoms would be forced into one another. Most of the examples we have studied so far have involved solid objects which deform very little when stressed.
Atomic and molecular characteristics explain and underlie the macroscopic characteristics of solids and fluids. This submicroscopic explanation is one theme of this text and is highlighted in the Things Great and Small features in Conservation of Momentum . See, for example, microscopic description of collisions and momentum or microscopic description of pressure in a gas. This present section is devoted entirely to the submicroscopic explanation of solids and liquids.
In contrast, liquids deform easily when stressed and do not spring back to their original shape once the force is removed because the atoms are free to slide about and change neighbors—that is, they flow (so they are a type of fluid), with the molecules held together by their mutual attraction. When a liquid is placed in a container with no lid on, it remains in the container (providing the container has no holes below the surface of the liquid!). Because the atoms are closely packed, liquids, like solids, resist compression.
Atoms in gases are separated by distances that are large compared with the size of the atoms. The forces between gas atoms are therefore very weak, except when the atoms collide with one another. Gases thus not only flow (and are therefore considered to be fluids) but they are relatively easy to compress because there is much space and little force between atoms. When placed in an open container gases, unlike liquids, will escape. The major distinction is that gases are easily compressed, whereas liquids are not. We shall generally refer to both gases and liquids simply as fluids , and make a distinction between them only when they behave differently.
Heat, cool, and compress atoms and molecules and watch as they change between solid, liquid, and gas phases.

What physical characteristic distinguishes a fluid from a solid?
Which of the following substances are fluids at room temperature: air, mercury, water, glass?
Why are gases easier to compress than liquids and solids?
How do gases differ from liquids?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?