| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Why does Earth keep on spinning? What started it spinning to begin with? And how does an ice skater manage to spin faster and faster simply by pulling her arms in? Why does she not have to exert a torque to spin faster? Questions like these have answers based in angular momentum, the rotational analog to linear momentum.
By now the pattern is clear—every rotational phenomenon has a direct translational analog. It seems quite reasonable, then, to define angular momentum as
This equation is an analog to the definition of linear momentum as . Units for linear momentum are while units for angular momentum are . As we would expect, an object that has a large moment of inertia , such as Earth, has a very large angular momentum. An object that has a large angular velocity , such as a centrifuge, also has a rather large angular momentum.
Angular momentum is completely analogous to linear momentum, first presented in Uniform Circular Motion and Gravitation . It has the same implications in terms of carrying rotation forward, and it is conserved when the net external torque is zero. Angular momentum, like linear momentum, is also a property of the atoms and subatomic particles.
Strategy
No information is given in the statement of the problem; so we must look up pertinent data before we can calculate . First, according to [link] , the formula for the moment of inertia of a sphere is
so that
Earth’s mass is and its radius is . The Earth’s angular velocity is, of course, exactly one revolution per day, but we must covert to radians per second to do the calculation in SI units.
Solution
Substituting known information into the expression for and converting to radians per second gives
Substituting rad for rev and for 1 day gives
Discussion
This number is large, demonstrating that Earth, as expected, has a tremendous angular momentum. The answer is approximate, because we have assumed a constant density for Earth in order to estimate its moment of inertia.
When you push a merry-go-round, spin a bike wheel, or open a door, you exert a torque. If the torque you exert is greater than opposing torques, then the rotation accelerates, and angular momentum increases. The greater the net torque, the more rapid the increase in . The relationship between torque and angular momentum is
This expression is exactly analogous to the relationship between force and linear momentum, . The equation is very fundamental and broadly applicable. It is, in fact, the rotational form of Newton’s second law.
[link] shows a Lazy Susan food tray being rotated by a person in quest of sustenance. Suppose the person exerts a 2.50 N force perpendicular to the lazy Susan’s 0.260-m radius for 0.150 s. (a) What is the final angular momentum of the lazy Susan if it starts from rest, assuming friction is negligible? (b) What is the final angular velocity of the lazy Susan, given that its mass is 4.00 kg and assuming its moment of inertia is that of a disk?
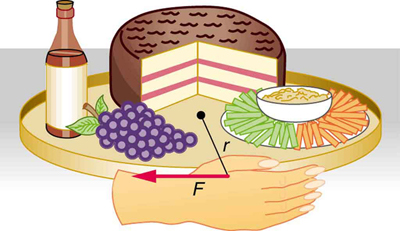
Strategy
We can find the angular momentum by solving for , and using the given information to calculate the torque. The final angular momentum equals the change in angular momentum, because the lazy Susan starts from rest. That is, . To find the final velocity, we must calculate from the definition of in .
Solution for (a)
Solving for gives
Because the force is perpendicular to , we see that , so that
Solution for (b)
The final angular velocity can be calculated from the definition of angular momentum,
Solving for and substituting the formula for the moment of inertia of a disk into the resulting equation gives
And substituting known values into the preceding equation yields
Discussion
Note that the imparted angular momentum does not depend on any property of the object but only on torque and time. The final angular velocity is equivalent to one revolution in 8.71 s (determination of the time period is left as an exercise for the reader), which is about right for a lazy Susan.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?