| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Uniform Circular Motion and Gravitation discussed only uniform circular motion, which is motion in a circle at constant speed and, hence, constant angular velocity. Recall that angular velocity was defined as the time rate of change of angle :
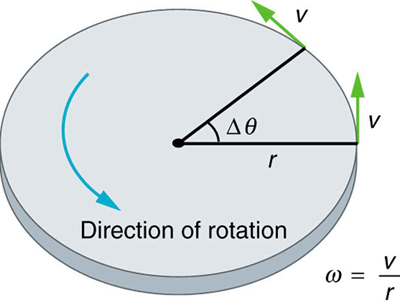
where is the angle of rotation as seen in [link] . The relationship between angular velocity and linear velocity was also defined in Rotation Angle and Angular Velocity as
or
where is the radius of curvature, also seen in [link] . According to the sign convention, the counter clockwise direction is considered as positive direction and clockwise direction as negative
Angular velocity is not constant when a skater pulls in her arms, when a child starts up a merry-go-round from rest, or when a computer’s hard disk slows to a halt when switched off. In all these cases, there is an angular acceleration , in which changes. The faster the change occurs, the greater the angular acceleration. Angular acceleration is defined as the rate of change of angular velocity. In equation form, angular acceleration is expressed as follows:
where is the change in angular velocity and is the change in time. The units of angular acceleration are , or . If increases, then is positive. If decreases, then is negative.
Suppose a teenager puts her bicycle on its back and starts the rear wheel spinning from rest to a final angular velocity of 250 rpm in 5.00 s. (a) Calculate the angular acceleration in . (b) If she now slams on the brakes, causing an angular acceleration of , how long does it take the wheel to stop?
Strategy for (a)
The angular acceleration can be found directly from its definition in because the final angular velocity and time are given. We see that is 250 rpm and is 5.00 s.
Solution for (a)
Entering known information into the definition of angular acceleration, we get
Because is in revolutions per minute (rpm) and we want the standard units of for angular acceleration, we need to convert from rpm to rad/s:
Entering this quantity into the expression for , we get
Strategy for (b)
In this part, we know the angular acceleration and the initial angular velocity. We can find the stoppage time by using the definition of angular acceleration and solving for , yielding
Solution for (b)
Here the angular velocity decreases from (250 rpm) to zero, so that is , and is given to be . Thus,
Discussion
Note that the angular acceleration as the girl spins the wheel is small and positive; it takes 5 s to produce an appreciable angular velocity. When she hits the brake, the angular acceleration is large and negative. The angular velocity quickly goes to zero. In both cases, the relationships are analogous to what happens with linear motion. For example, there is a large deceleration when you crash into a brick wall—the velocity change is large in a short time interval.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?