| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Rolling motion
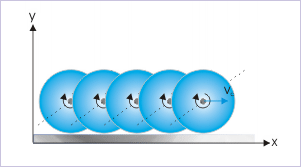
The different particles on the rim of the disk - what to talk of other particles constituting it - transverse (cover) different paths in the ground reference. The figure below captures the position of a particle at the contact point over a period, as the disk rolls on the horizontal surface. Evidently, the particle at the rim describes a curved path, whereas the center of mass describes a straight line path. This means that rolling motion is not a pure translation either. Remember that all particles in pure translation have same motion along a straight line. In the nutshell, we can conclude that rolling of the disk is neither a pure rotation nor a pure translation as seen in the frame of reference attached to the ground.
Rolling motion
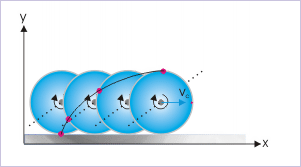
The path of the particle on the rim points to an interesting aspect of rolling motion. Since it has been assumed that the center of mass of the disk is moving with uniform velocity, we can infer from the nature of the path (as drawn in the figure above) that particle on the rim of the disk are actually moving with different velocities depending on its position with respect to the point of contact. The velocity of a particle near the point of contact is minimum as it covers smaller distance (length of the curve) and the velocity of the same particle near the top is greater as it covers the longer distance in a given time. This is also evident from the fact that curve is steeper near contact point and flatter near the top point. In simple words, we can conclude that the particles on the rim of the disk are having varying linear velocities - starting from zero at the contact to a maximum value at the top of the disk.
Analysis of rolling motion can be undertaken with two different perspectives :
Rolling is considered as the combination of pure rotation and pure translation.
1: Pure rotation
For pure rotation, we consider that the rotating disk rotates about a fixed axis with angular velocity, "ω" such that :
Each particle of the rotating disk moves with same angular velocity. In the figure, we have shown the linear velocities of particles occupying four positions on the rim with appropriate vectors. The magnitude of velocity of these four particles on the rim, resulting from pure rotation, is given by :

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics for k-12' conversation and receive update notifications?