| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In the AP ® Physics 2 course, you will continue your journey by studying fluid dynamics, which explains why rising smoke curls and twists and how the body regulates blood flow. The next stop is thermodynamics, the study of heat transfer—energy in transit—that can be used to do work. Basic physical laws govern how heat transfers and its efficiency. Then you will learn more about electric phenomena as you delve into electromagnetism. An electric current produces a magnetic field; similarly, a magnetic field produces a current. This phenomenon, known as magnetic induction, is essential to our technological society. The generators in cars and nuclear plants use magnetism to generate a current. Other devices that use magnetism to induce currents include pickup coils in electric guitars, transformers of every size, certain microphones, airport security gates, and damping mechanisms on sensitive chemical balances. From electromagnetism you will continue your journey to optics, the study of light. You already know that visible light is the type of electromagnetic waves to which our eyes respond. Through vision, light can evoke deep emotions, such as when we view a magnificent sunset or glimpse a rainbow breaking through the clouds. Optics is concerned with the generation and propagation of light. The quantum mechanics, atomic physics, and nuclear physics are at the end of your journey. These areas of physics have been developed at the end of the 19th and early 20th centuries and deal with submicroscopic objects. Because these objects are smaller than we can observe directly with our senses and generally must be observed with the aid of instruments, parts of these physics areas may seem foreign and bizarre to you at first. However, we have experimentally confirmed most of the ideas in these areas of physics.
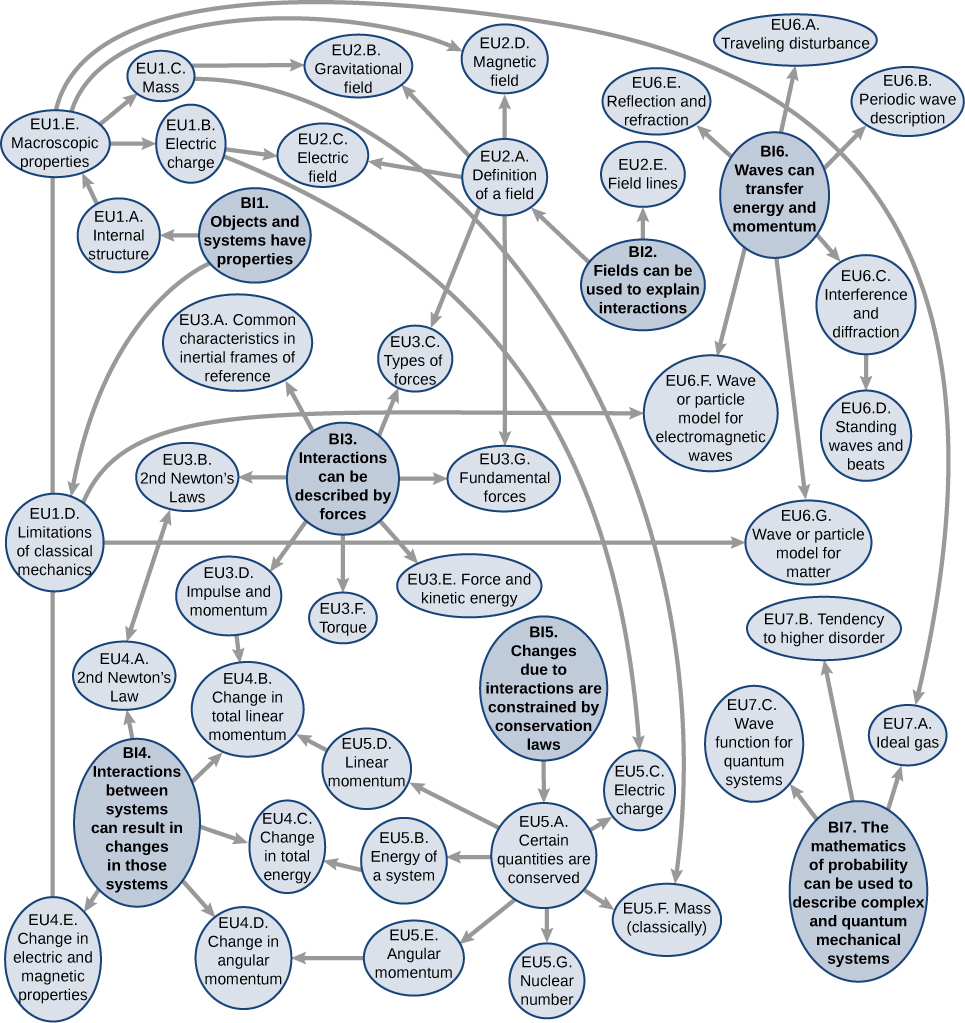
AP ® Physics is a challenging course. After all, you are taking physics at the introductory college level. You will discover that some concepts are more difficult to understand than others; most students, for example, struggle to understand rotational motion and angular momentum or particle-wave duality. The AP ® curriculum promotes depth of understanding over breadth of content, and to make your exploration of topics more manageable, concepts are organized around seven major themes called the Big Ideas that apply to all levels of physical systems and interactions between them (see web diagram below). Each Big Idea identifies enduring understandings (EU), essential knowledge (EK), and illustrative examples that support key concepts and content. Simple descriptions define the focus of each Big Idea.
Doing college work is not easy, but completion of AP ® classes is a reliable predictor of college success and prepares you for subsequent courses. The more you engage in the subject, the easier your journey through the curriculum will be. Bring your enthusiasm to class every day along with your notebook, pencil, and calculator. Prepare for class the day before, and review concepts daily. Form a peer study group and ask your teacher for extra help if necessary. The AP ® lab program focuses on more open-ended, student-directed, and inquiry-based lab investigations designed to make you think, ask questions, and analyze data like scientists. You will develop critical thinking and reasoning skills and apply different means of communicating information. By the time you sit for the AP ® exam in May, you will be fluent in the language of physics; because you have been doing real science, you will be ready to show what you have learned. Along the way, you will find the study of the world around us to be one of the most relevant and enjoyable experiences of your high school career.
Irina Lyublinskaya, PhD
Professor of Science Education
The AP ® curriculum was designed to allow instructors flexibility in their approach to teaching the physics courses. College Physics for AP ® Courses helps you orient students as they delve deeper into the world of physics. Each chapter includes a Connection for AP ® Courses introduction that describes the AP ® Physics Big Ideas, enduring understandings, and essential knowledge addressed in that chapter.
Each section starts with specific AP ® learning objectives and includes essential concepts, illustrative examples, and science practices, along with suggestions for applying the learning objectives through take-home experiments, virtual lab investigations, and activities and questions for preparation and review. At the end of each section, students will find the Test Prep for AP ® courses with multiple-choice and open-response questions addressing AP® learning objectives to help them prepare for the AP ® exam.
College Physics for AP ® Courses has been written to engage students in their exploration of physics and help them relate what they learn in the classroom to their lives outside of it. Physics underlies much of what is happening today in other sciences and in technology. Thus, the book content includes interesting facts and ideas that go beyond the scope of the AP ® course. The AP ® Connection in each chapter directs students to the material they should focus on for the AP ® exam, and what content—although interesting—is not part of the AP ® curriculum. Physics is a beautiful and fascinating science. It is in your hands to engage and inspire your students to dive into an amazing world of physics, so they can enjoy it beyond just preparation for the AP ® exam.
Irina Lyublinskaya, PhD
Professor of Science Education

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?