| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
| Material | Coefficient of linear expansion | Coefficient of volume expansion |
|---|---|---|
| Solids | ||
| Aluminum | ||
| Brass | ||
| Copper | ||
| Gold | ||
| Iron or Steel | ||
| Invar (Nickel-iron alloy) | ||
| Lead | ||
| Silver | ||
| Glass (ordinary) | ||
| Glass (Pyrex®) | ||
| Quartz | ||
| Concrete, Brick | ||
| Marble (average) | ||
| Liquids | ||
| Ether | ||
| Ethyl alcohol | ||
| Petrol | ||
| Glycerin | ||
| Mercury | ||
| Water | ||
| Gases | ||
| Air and most other gases at atmospheric pressure |
The main span of San Francisco’s Golden Gate Bridge is 1275 m long at its coldest. The bridge is exposed to temperatures ranging from to . What is its change in length between these temperatures? Assume that the bridge is made entirely of steel.
Strategy
Use the equation for linear thermal expansion to calculate the change in length , . Use the coefficient of linear expansion, , for steel from [link] , and note that the change in temperature, , is .
Solution
Plug all of the known values into the equation to solve for .
Discussion
Although not large compared with the length of the bridge, this change in length is observable. It is generally spread over many expansion joints so that the expansion at each joint is small.
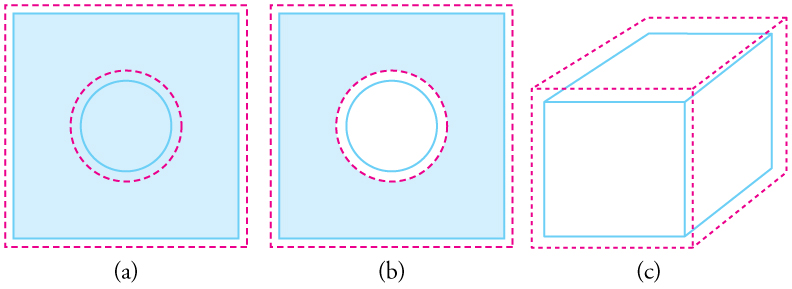
Objects expand in all dimensions, as illustrated in [link] . That is, their areas and volumes, as well as their lengths, increase with temperature. Holes also get larger with temperature. If you cut a hole in a metal plate, the remaining material will expand exactly as it would if the plug was still in place. The plug would get bigger, and so the hole must get bigger too. (Think of the ring of neighboring atoms or molecules on the wall of the hole as pushing each other farther apart as temperature increases. Obviously, the ring of neighbors must get slightly larger, so the hole gets slightly larger).
For small temperature changes, the change in area is given by
where is the change in area , is the change in temperature, and is the coefficient of linear expansion, which varies slightly with temperature.
The change in volume is very nearly . This equation is usually written as
where is the coefficient of volume expansion and . Note that the values of in [link] are almost exactly equal to .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?