| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
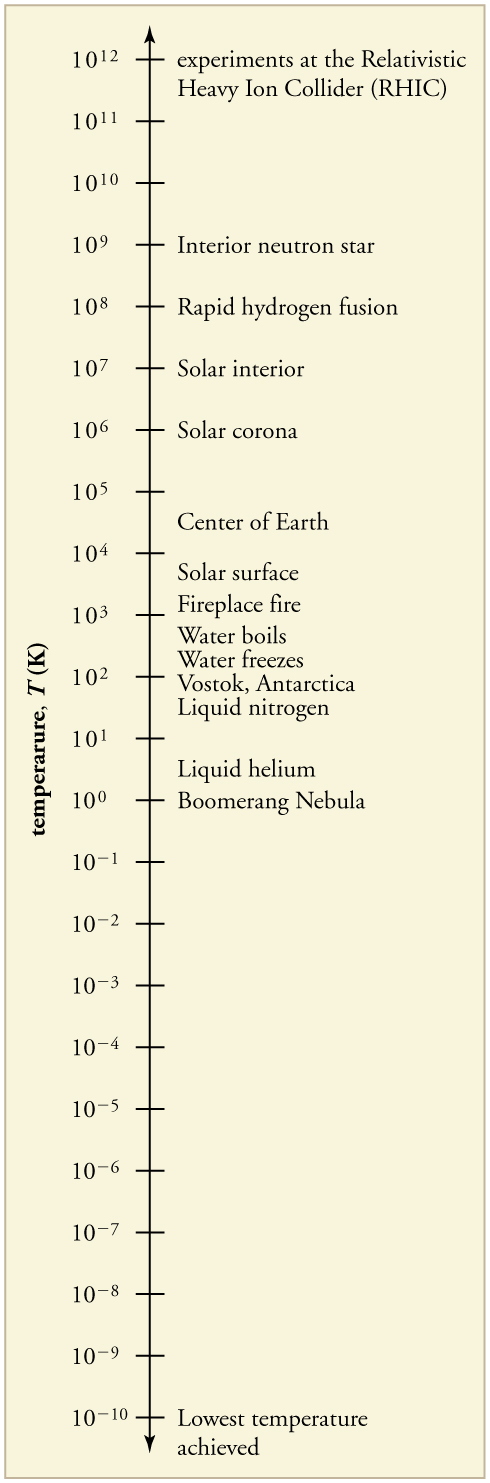
The lowest temperatures ever recorded have been measured during laboratory experiments: at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (USA), and at Helsinki University of Technology (Finland). In comparison, the coldest recorded place on Earth’s surface is Vostok, Antarctica at 183 K , and the coldest place (outside the lab) known in the universe is the Boomerang Nebula, with a temperature of 1 K.
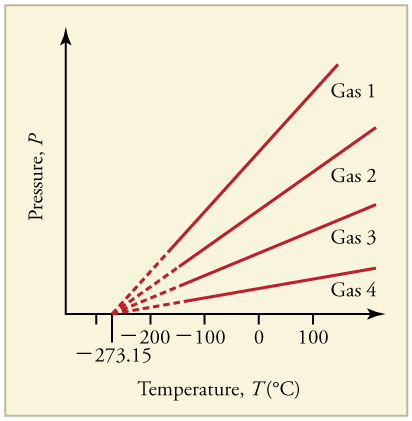
What is absolute zero? Absolute zero is the temperature at which all molecular motion has ceased. The concept of absolute zero arises from the behavior of gases. [link] shows how the pressure of gases at a constant volume decreases as temperature decreases. Various scientists have noted that the pressures of gases extrapolate to zero at the same temperature, . This extrapolation implies that there is a lowest temperature. This temperature is called absolute zero . Today we know that most gases first liquefy and then freeze, and it is not actually possible to reach absolute zero. The numerical value of absolute zero temperature is or 0 K.
Thermometers actually take their own temperature, not the temperature of the object they are measuring. This raises the question of how we can be certain that a thermometer measures the temperature of the object with which it is in contact. It is based on the fact that any two systems placed in thermal contact (meaning heat transfer can occur between them) will reach the same temperature. That is, heat will flow from the hotter object to the cooler one until they have exactly the same temperature. The objects are then in thermal equilibrium , and no further changes will occur. The systems interact and change because their temperatures differ, and the changes stop once their temperatures are the same. Thus, if enough time is allowed for this transfer of heat to run its course, the temperature a thermometer registers does represent the system with which it is in thermal equilibrium. Thermal equilibrium is established when two bodies are in contact with each other and can freely exchange energy.
Furthermore, experimentation has shown that if two systems, A and B, are in thermal equilibrium with each another, and B is in thermal equilibrium with a third system C, then A is also in thermal equilibrium with C. This conclusion may seem obvious, because all three have the same temperature, but it is basic to thermodynamics. It is called the zeroth law of thermodynamics .
If two systems, A and B, are in thermal equilibrium with each other, and B is in thermal equilibrium with a third system, C, then A is also in thermal equilibrium with C.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?