| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
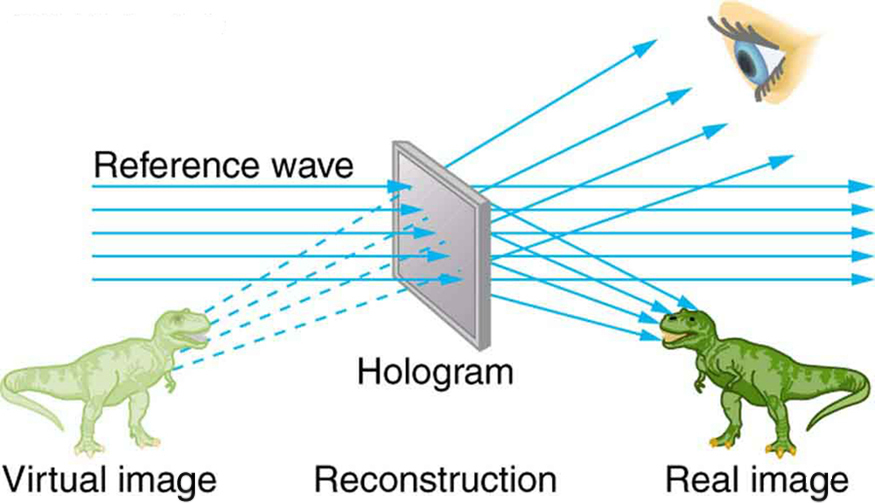
The hologram illustrated in [link] is a transmission hologram. Holograms that are viewed with reflected light, such as the white light holograms on credit cards, are reflection holograms and are more common. White light holograms often appear a little blurry with rainbow edges, because the diffraction patterns of various colors of light are at slightly different locations due to their different wavelengths. Further uses of holography include all types of 3-D information storage, such as of statues in museums and engineering studies of structures and 3-D images of human organs. Invented in the late 1940s by Dennis Gabor (1900–1970), who won the 1971 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work, holography became far more practical with the development of the laser. Since lasers produce coherent single-wavelength light, their interference patterns are more pronounced. The precision is so great that it is even possible to record numerous holograms on a single piece of film by just changing the angle of the film for each successive image. This is how the holograms that move as you walk by them are produced—a kind of lensless movie.
In a similar way, in the medical field, holograms have allowed complete 3-D holographic displays of objects from a stack of images. Storing these images for future use is relatively easy. With the use of an endoscope, high-resolution 3-D holographic images of internal organs and tissues can be made.
A sample of hydrogen gas confined to a tube is initially at room temperature. As the gas is heated, the observer notices that the gas begins to glow with a pale pink color. Careful study of the spectrum shows that the light spectrum is not continuous. Instead, the hydrogen gas is only emitting visible wavelength photons of four specific colors, which combine to form the overall color to the human eye. What is the best way to explain this behavior?
(b)
A rock is illuminated with high energy ultraviolet light. This causes the rock to emit visible light. Explain what is happening in the atomic substructure of the rock that causes this effect, which we call fluorescence.
Which of the following is the best way of explaining why the leaves on a given tree are green?
(a)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?