| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
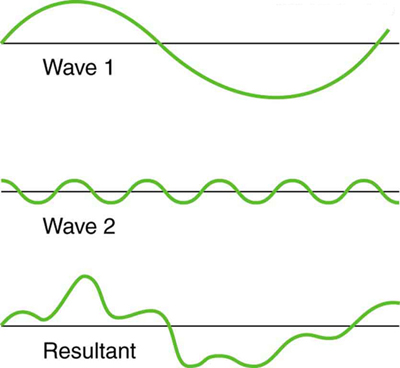
An example of the superposition of two dissimilar waves is shown in [link] . Here again, the disturbances add and subtract, producing a more complicated looking wave.
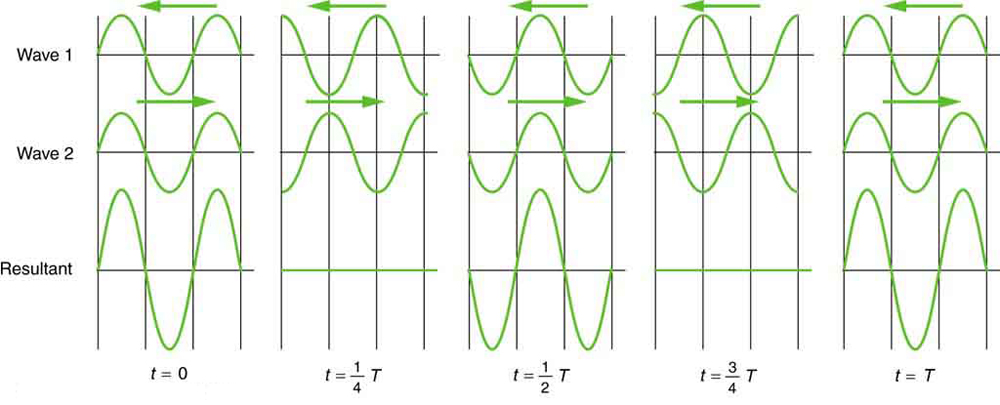
Sometimes waves do not seem to move; rather, they just vibrate in place. Unmoving waves can be seen on the surface of a glass of milk in a refrigerator, for example. Vibrations from the refrigerator motor create waves on the milk that oscillate up and down but do not seem to move across the surface. These waves are formed by the superposition of two or more moving waves, such as illustrated in [link] for two identical waves moving in opposite directions. The waves move through each other with their disturbances adding as they go by. If the two waves have the same amplitude and wavelength, then they alternate between constructive and destructive interference. The resultant looks like a wave standing in place and, thus, is called a standing wave . Waves on the glass of milk are one example of standing waves. There are other standing waves, such as on guitar strings and in organ pipes. With the glass of milk, the two waves that produce standing waves may come from reflections from the side of the glass.
A closer look at earthquakes provides evidence for conditions appropriate for resonance, standing waves, and constructive and destructive interference. A building may be vibrated for several seconds with a driving frequency matching that of the natural frequency of vibration of the building—producing a resonance resulting in one building collapsing while neighboring buildings do not. Often buildings of a certain height are devastated while other taller buildings remain intact. The building height matches the condition for setting up a standing wave for that particular height. As the earthquake waves travel along the surface of Earth and reflect off denser rocks, constructive interference occurs at certain points. Often areas closer to the epicenter are not damaged while areas farther away are damaged.
Standing waves are also found on the strings of musical instruments and are due to reflections of waves from the ends of the string. [link] and [link] show three standing waves that can be created on a string that is fixed at both ends. Nodes are the points where the string does not move; more generally, nodes are where the wave disturbance is zero in a standing wave. The fixed ends of strings must be nodes, too, because the string cannot move there. The word antinode is used to denote the location of maximum amplitude in standing waves. Standing waves on strings have a frequency that is related to the propagation speed of the disturbance on the string. The wavelength is determined by the distance between the points where the string is fixed in place.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?