| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
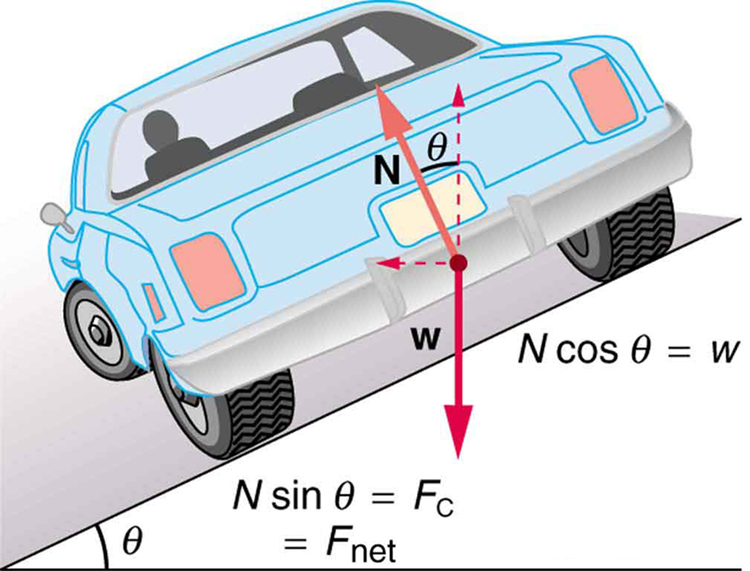
Because the car does not leave the surface of the road, the net vertical force must be zero, meaning that the vertical components of the two external forces must be equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. From the figure, we see that the vertical component of the normal force is , and the only other vertical force is the car's weight. These must be equal in magnitude; thus,
Now we can combine the last two equations to eliminate and get an expression for , as desired. Solving the second equation for , and substituting this into the first yields
Taking the inverse tangent gives
This expression can be understood by considering how depends on and . A large will be obtained for a large and a small . That is, roads must be steeply banked for high speeds and sharp curves. Friction helps, because it allows you to take the curve at greater or lower speed than if the curve is frictionless. Note that does not depend on the mass of the vehicle.
Curves on some test tracks and race courses, such as the Daytona International Speedway in Florida, are very steeply banked. This banking, with the aid of tire friction and very stable car configurations, allows the curves to be taken at very high speed. To illustrate, calculate the speed at which a 100 m radius curve banked at 65.0° should be driven if the road is frictionless.
Strategy
We first note that all terms in the expression for the ideal angle of a banked curve except for speed are known; thus, we need only rearrange it so that speed appears on the left-hand side and then substitute known quantities.
Solution
Starting with
we get
Noting that tan 65.0º = 2.14, we obtain
Discussion
This is just about 165 km/h, consistent with a very steeply banked and rather sharp curve. Tire friction enables a vehicle to take the curve at significantly higher speeds.
Calculations similar to those in the preceding examples can be performed for a host of interesting situations in which centripetal force is involved—a number of these are presented in this chapter's Problems and Exercises.
Ask a friend or relative to swing a golf club or a tennis racquet. Take appropriate measurements to estimate the centripetal acceleration of the end of the club or racquet. You may choose to do this in slow motion.
Move the sun, earth, moon and space station to see how it affects their gravitational forces and orbital paths. Visualize the sizes and distances between different heavenly bodies, and turn off gravity to see what would happen without it!

which can also be expressed as

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?