| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
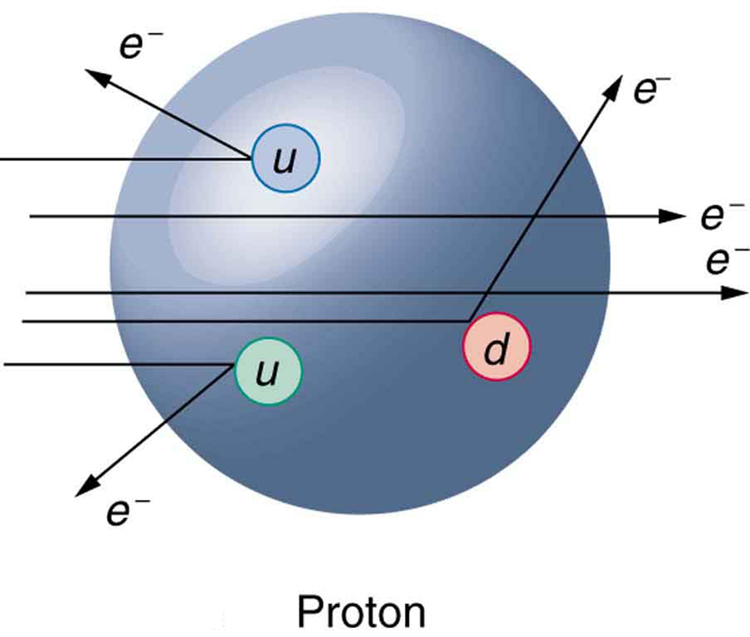
At first, physicists expected that, with sufficient energy, we should be able to free quarks and observe them directly. This has not proved possible. There is still no direct observation of a fractional charge or any isolated quark. When large energies are put into collisions, other particles are created—but no quarks emerge. There is nearly direct evidence for quarks that is quite compelling. By 1967, experiments at SLAC scattering 20-GeV electrons from protons had produced results like Rutherford had obtained for the nucleus nearly 60 years earlier. The SLAC scattering experiments showed unambiguously that there were three pointlike (meaning they had sizes considerably smaller than the probe's wavelength) charges inside the proton as seen in [link] . This evidence made all but the most skeptical admit that there was validity to the quark substructure of hadrons.
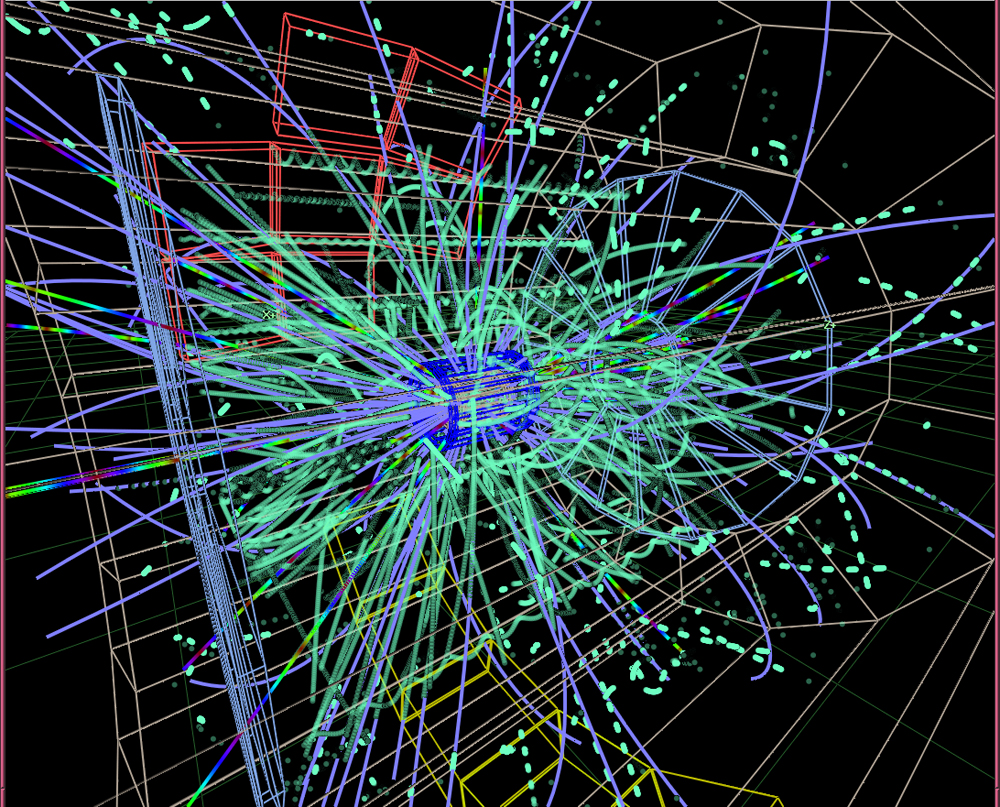
More recent and higher-energy experiments have produced jets of particles in collisions, highly suggestive of three quarks in a nucleon. Since the quarks are very tightly bound, energy put into separating them pulls them only so far apart before it starts being converted into other particles. More energy produces more particles, not a separation of quarks. Conservation of momentum requires that the particles come out in jets along the three paths in which the quarks were being pulled. Note that there are only three jets, and that other characteristics of the particles are consistent with the three-quark substructure.
The quark model actually lost some of its early popularity because the original model with three quarks had to be modified. The up and down quarks seemed to compose normal matter as seen in [link] , while the single strange quark explained strangeness. Why didn't it have a counterpart? A fourth quark flavor called charm ( c ) was proposed as the counterpart of the strange quark to make things symmetric—there would be two normal quarks ( u and d ) and two exotic quarks ( s and c ). Furthermore, at that time only four leptons were known, two normal and two exotic. It was attractive that there would be four quarks and four leptons. The problem was that no known particles contained a charmed quark. Suddenly, in November of 1974, two groups (one headed by C. C. Ting at Brookhaven National Laboratory and the other by Burton Richter at SLAC) independently and nearly simultaneously discovered a new meson with characteristics that made it clear that its substructure is . It was called J by one group and psi ( ) by the other and now is known as the meson. Since then, numerous particles have been discovered containing the charmed quark, consistent in every way with the quark model. The discovery of the meson had such a rejuvenating effect on quark theory that it is now called the November Revolution. Ting and Richter shared the 1976 Nobel Prize.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?