| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
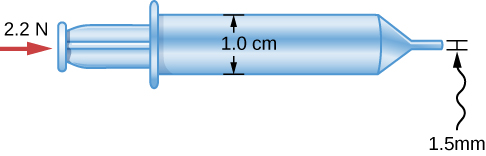
A horizontally oriented squirt toy contains a 1.0-cm-diameter barrel for the water. A 2.2-N force on the plunger forces water down the barrel and into a 1.5-mm-diameter opening at the end of the squirt gun. In addition to the force pushing on the plunger, pressure from the atmosphere is also present at both ends of the gun, pushing the plunger in and also pushing the water back in to the narrow opening at the other end. Assuming that the water is moving very slowly in the barrel, with what speed does it emerge from the toy?
Solution
First, find the cross-sectional areas for each part of the toy. The wider part is
Next, we will find the area of the narrower part of the toy:
The pressure pushing on the barrel is equal to the sum of the pressure from the atmosphere ( ) and the pressure created by the 2.2-N force.
The pressure pushing on the smaller end of the toy is simply the pressure from the atmosphere:
Since the gun is oriented horizontally ( ), we can ignore the potential energy term in Bernoulli's equation, so the equation becomes:
The problem states that the water is moving very slowly in the barrel. That means we can make the approximation that , which we will justify mathematically.
How accurate is our assumption that the water velocity in the barrel is approximately zero? Check using the continuity equation:
How does the kinetic energy per unit volume term for water in the barrel fit into Bernoulli's equation?
As you can see, the kinetic energy per unit volume term for water in the barrel is very small (14) compared to the other terms (which are all at least 1000 times larger). Another way to look at this is to consider the ratio of the two terms that represent kinetic energy per unit volume:
Remember that from the continuity equation
Thus, the ratio of the kinetic energy per unit volume terms depends on the fourth power of the ratio of the diameters:
In this case, the diameter of the barrel ( d 2 ) is 6.7 times larger than the diameter of the opening at the end of the toy ( d 1 ), which makes the kinetic energy per unit volume term for water in the barrel times smaller. We can usually neglect such small terms in addition or subtraction without a significant loss of accuracy.
Power is the rate at which work is done or energy in any form is used or supplied. To see the relationship of power to fluid flow, consider Bernoulli's equation:
All three terms have units of energy per unit volume, as discussed in the previous section. Now, considering units, if we multiply energy per unit volume by flow rate (volume per unit time), we get units of power. That is, . This means that if we multiply Bernoulli's equation by flow rate , we get power. In equation form, this is

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?