| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Although varies from to , depending on latitude, altitude, underlying geological formations, and local topography, the average value of will be used in this text unless otherwise specified. The direction of the acceleration due to gravity is downward (towards the center of Earth) . In fact, its direction defines what we call vertical. Note that whether the acceleration in the kinematic equations has the value or depends on how we define our coordinate system. If we define the upward direction as positive, then , and if we define the downward direction as positive, then .
The best way to see the basic features of motion involving gravity is to start with the simplest situations and then progress toward more complex ones. So we start by considering straight up and down motion with no air resistance or friction. These assumptions mean that the velocity (if there is any) is vertical. If the object is dropped, we know the initial velocity is zero. Once the object has left contact with whatever held or threw it, the object is in free-fall. Under these circumstances, the motion is one-dimensional and has constant acceleration of magnitude . We will also represent vertical displacement with the symbol and use for horizontal displacement.
A person standing on the edge of a high cliff throws a rock straight up with an initial velocity of 13.0 m/s . The rock misses the edge of the cliff as it falls back to Earth. Calculate the position and velocity of the rock 1.00 s, 2.00 s, and 3.00 s after it is thrown, neglecting the effects of air resistance.
Strategy
Draw a sketch.
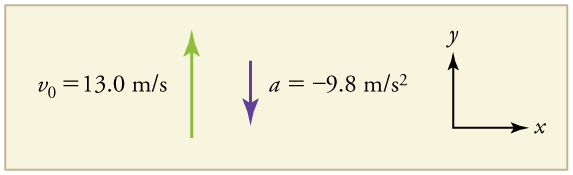
We are asked to determine the position at various times. It is reasonable to take the initial position to be zero. This problem involves one-dimensional motion in the vertical direction. We use plus and minus signs to indicate direction, with up being positive and down negative. Since up is positive, and the rock is thrown upward, the initial velocity must be positive too. The acceleration due to gravity is downward, so is negative. It is crucial that the initial velocity and the acceleration due to gravity have opposite signs. Opposite signs indicate that the acceleration due to gravity opposes the initial motion and will slow and eventually reverse it.
Since we are asked for values of position and velocity at three times, we will refer to these as and ; and ; and and .
Solution for Position
1. Identify the knowns. We know that ; ; ; and .
2. Identify the best equation to use. We will use because it includes only one unknown, (or , here), which is the value we want to find.
3. Plug in the known values and solve for .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?