| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
The information presented in this section supports the following AP® learning objectives and science practices:
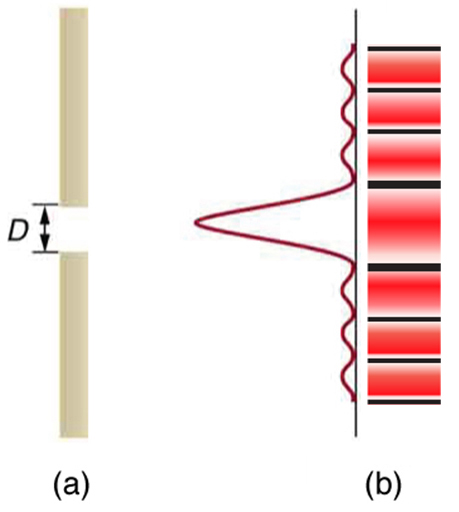
Light passing through a single slit forms a diffraction pattern somewhat different from those formed by double slits or diffraction gratings. [link] shows a single slit diffraction pattern. Note that the central maximum is larger than those on either side, and that the intensity decreases rapidly on either side. In contrast, a diffraction grating produces evenly spaced lines that dim slowly on either side of center.
The analysis of single slit diffraction is illustrated in [link] . Here we consider light coming from different parts of the same slit. According to Huygens’s principle, every part of the wavefront in the slit emits wavelets. These are like rays that start out in phase and head in all directions. (Each ray is perpendicular to the wavefront of a wavelet.) Assuming the screen is very far away compared with the size of the slit, rays heading toward a common destination are nearly parallel. When they travel straight ahead, as in [link] (a), they remain in phase, and a central maximum is obtained. However, when rays travel at an angle relative to the original direction of the beam, each travels a different distance to a common location, and they can arrive in or out of phase. In [link] (b), the ray from the bottom travels a distance of one wavelength farther than the ray from the top. Thus a ray from the center travels a distance farther than the one on the left, arrives out of phase, and interferes destructively. A ray from slightly above the center and one from slightly above the bottom will also cancel one another. In fact, each ray from the slit will have another to interfere destructively, and a minimum in intensity will occur at this angle. There will be another minimum at the same angle to the right of the incident direction of the light.
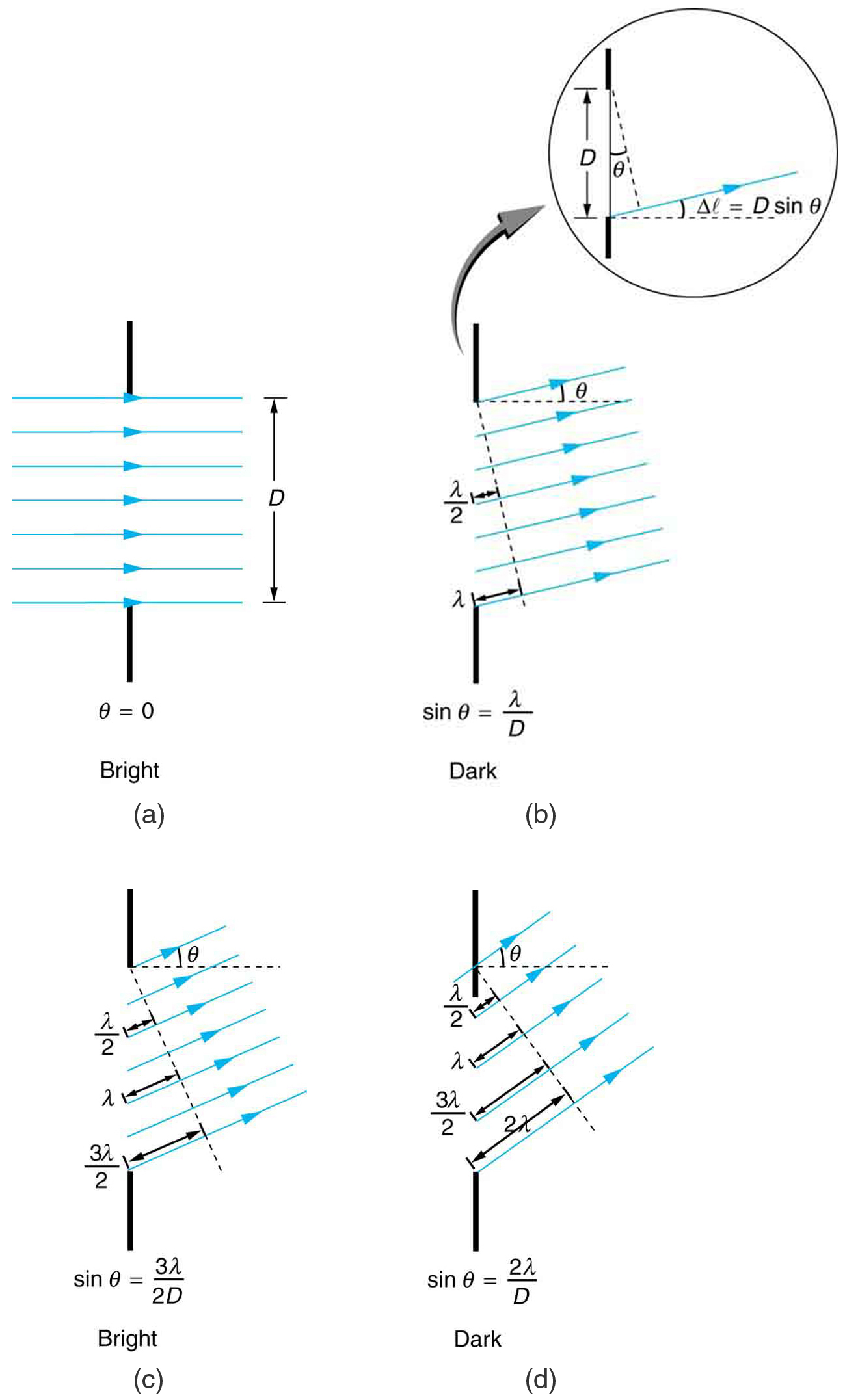
At the larger angle shown in [link] (c), the path lengths differ by for rays from the top and bottom of the slit. One ray travels a distance different from the ray from the bottom and arrives in phase, interfering constructively. Two rays, each from slightly above those two, will also add constructively. Most rays from the slit will have another to interfere with constructively, and a maximum in intensity will occur at this angle. However, all rays do not interfere constructively for this situation, and so the maximum is not as intense as the central maximum. Finally, in [link] (d), the angle shown is large enough to produce a second minimum. As seen in the figure, the difference in path length for rays from either side of the slit is , and we see that a destructive minimum is obtained when this distance is an integral multiple of the wavelength.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?