| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:

In classical physics, momentum is a simple product of mass and velocity. However, we saw in the last section that when special relativity is taken into account, massive objects have a speed limit. What effect do you think mass and velocity have on the momentum of objects moving at relativistic speeds?
Momentum is one of the most important concepts in physics. The broadest form of Newton’s second law is stated in terms of momentum. Momentum is conserved whenever the net external force on a system is zero. This makes momentum conservation a fundamental tool for analyzing collisions. All of Work, Energy, and Energy Resources is devoted to momentum, and momentum has been important for many other topics as well, particularly where collisions were involved. We will see that momentum has the same importance in modern physics. Relativistic momentum is conserved, and much of what we know about subatomic structure comes from the analysis of collisions of accelerator-produced relativistic particles.
The first postulate of relativity states that the laws of physics are the same in all inertial frames. Does the law of conservation of momentum survive this requirement at high velocities? The answer is yes, provided that the momentum is defined as follows.
Relativistic momentum is classical momentum multiplied by the relativistic factor .
where is the rest mass of the object, is its velocity relative to an observer, and the relativistic factor
Note that we use for velocity here to distinguish it from relative velocity between observers. Only one observer is being considered here. With defined in this way, total momentum is conserved whenever the net external force is zero, just as in classical physics. Again we see that the relativistic quantity becomes virtually the same as the classical at low velocities. That is, relativistic momentum becomes the classical at low velocities, because is very nearly equal to 1 at low velocities.
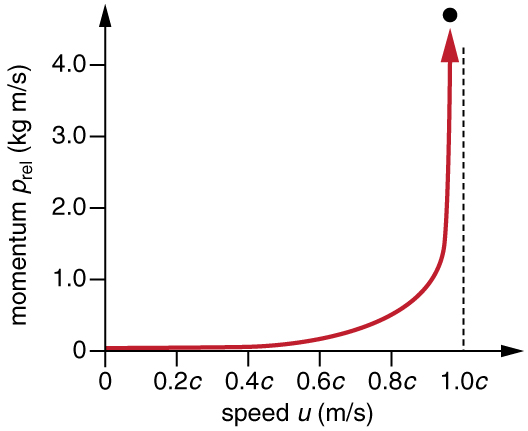
Relativistic momentum has the same intuitive feel as classical momentum. It is greatest for large masses moving at high velocities, but, because of the factor , relativistic momentum approaches infinity as approaches . (See [link] .) This is another indication that an object with mass cannot reach the speed of light. If it did, its momentum would become infinite, an unreasonable value.
The relativistically correct definition of momentum as is sometimes taken to imply that mass varies with velocity: , particularly in older textbooks. However, note that is the mass of the object as measured by a person at rest relative to the object. Thus, is defined to be the rest mass, which could be measured at rest, perhaps using gravity. When a mass is moving relative to an observer, the only way that its mass can be determined is through collisions or other means in which momentum is involved. Since the mass of a moving object cannot be determined independently of momentum, the only meaningful mass is rest mass. Thus, when we use the term mass, assume it to be identical to rest mass.
Relativistic momentum is defined in such a way that the conservation of momentum will hold in all inertial frames. Whenever the net external force on a system is zero, relativistic momentum is conserved, just as is the case for classical momentum. This has been verified in numerous experiments.
In Relativistic Energy , the relationship of relativistic momentum to energy is explored. That subject will produce our first inkling that objects without mass may also have momentum.
What is the momentum of an electron traveling at a speed ? The rest mass of the electron is .
How does modern relativity modify the law of conservation of momentum?
Is it possible for an external force to be acting on a system and relativistic momentum to be conserved? Explain.
Find the momentum of a helium nucleus having a mass of that is moving at .
What is the momentum of an electron traveling at ?
(a) Find the momentum of a asteroid heading towards the Earth at . (b) Find the ratio of this momentum to the classical momentum. (Hint: Use the approximation that at low velocities.)
(a) .
(b) Ratio of relativistic to classical momenta equals 1.000000005 (extra digits to show small effects)
(a) What is the momentum of a 2000 kg satellite orbiting at 4.00 km/s? (b) Find the ratio of this momentum to the classical momentum. (Hint: Use the approximation that at low velocities.)
What is the velocity of an electron that has a momentum of ? Note that you must calculate the velocity to at least four digits to see the difference from .
Find the velocity of a proton that has a momentum of
(a) Calculate the speed of a particle of dust that has the same momentum as a proton moving at . (b) What does the small speed tell us about the mass of a proton compared to even a tiny amount of macroscopic matter?
(a)
(b) The small speed tells us that the mass of a proton is substantially smaller than that of even a tiny amount of macroscopic matter!
(a) Calculate for a proton that has a momentum of (b) What is its speed? Such protons form a rare component of cosmic radiation with uncertain origins.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?