| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Plan an experiment to demonstrate electrostatic induction using household items, like balloons, woolen cloth, aluminum drink cans, or foam cups. Explain the process of induction in your experiment by discussing details of (and making diagrams relating to) the movement and alignment of charges.
Make sparks fly with John Travoltage. Wiggle Johnnie's foot and he picks up charges from the carpet. Bring his hand close to the door knob and get rid of the excess charge.

Some students experimenting with an uncharged metal sphere want to give the sphere a net charge using a charged aluminum pie plate. Which of the following steps would give the sphere a net charge of the same sign as the pie plate?
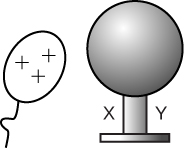
When the balloon is brought closer to the sphere, there will be a redistribution of charges. What is this phenomenon called?
(c)
What will be the charge at Y (i.e., the part of the sphere furthest from the balloon)?
What will be the net charge on the sphere?
(c)
If Y is grounded while the balloon is still close to X, which of the following will be true?
If the balloon is moved away after grounding, what will be the net charge on the sphere?
(b)
A positively charged rod is used to charge a sphere by induction. Which of the following is true?
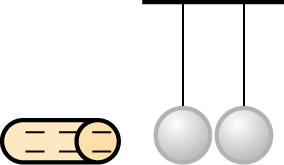
As shown in the figure above, two metal balls are suspended and a negatively charged rod is brought close to them.
a) Ball 1 will have positive charge and Ball 2 will have negative charge. b) The negatively charged rod attracts positive charge of Ball 1. The electrons of Ball 1 are transferred to Ball 2, making it negatively charged. c) If Ball 2 is grounded while the rod is still there, it will lose its negative charge to the ground. d) Yes, Ball 1 will be positively charged and Ball 2 will be negatively charge.
Two experiments are performed using positively charged glass rods and neutral electroscopes. In the first experiment the rod is brought in contact with the electroscope. In the second experiment the rod is only brought close to the electroscope but not in contact. However, while the rod is close, the electroscope is momentarily grounded and then the rod is removed. In both experiments the needles of the electroscopes deflect, which indicates the presence of charges.
An eccentric inventor attempts to levitate by first placing a large negative charge on himself and then putting a large positive charge on the ceiling of his workshop. Instead, while attempting to place a large negative charge on himself, his clothes fly off. Explain.
If you have charged an electroscope by contact with a positively charged object, describe how you could use it to determine the charge of other objects. Specifically, what would the leaves of the electroscope do if other charged objects were brought near its knob?
When a glass rod is rubbed with silk, it becomes positive and the silk becomes negative—yet both attract dust. Does the dust have a third type of charge that is attracted to both positive and negative? Explain.
Why does a car always attract dust right after it is polished? (Note that car wax and car tires are insulators.)
Describe how a positively charged object can be used to give another object a negative charge. What is the name of this process?
What is grounding? What effect does it have on a charged conductor? On a charged insulator?
Suppose a speck of dust in an electrostatic precipitator has protons in it and has a net charge of –5.00 nC (a very large charge for a small speck). How many electrons does it have?
An amoeba has protons and a net charge of 0.300 pC. (a) How many fewer electrons are there than protons? (b) If you paired them up, what fraction of the protons would have no electrons?
A 50.0 g ball of copper has a net charge of . What fraction of the copper's electrons has been removed? (Each copper atom has 29 protons, and copper has an atomic mass of 63.5.)
What net charge would you place on a 100 g piece of sulfur if you put an extra electron on 1 in of its atoms? (Sulfur has an atomic mass of 32.1.)
How many coulombs of positive charge are there in 4.00 kg of plutonium, given its atomic mass is 244 and that each plutonium atom has 94 protons?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?