| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
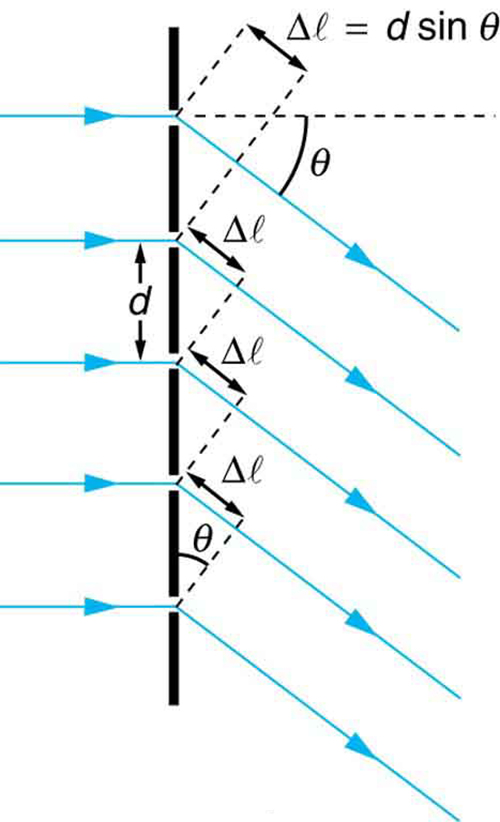
where is the distance between slits in the grating, is the wavelength of light, and is the order of the maximum. Note that this is exactly the same equation as for double slits separated by . However, the slits are usually closer in diffraction gratings than in double slits, producing fewer maxima at larger angles.
Where are diffraction gratings used? Diffraction gratings are key components of monochromators used, for example, in optical imaging of particular wavelengths from biological or medical samples. A diffraction grating can be chosen to specifically analyze a wavelength emitted by molecules in diseased cells in a biopsy sample or to help excite strategic molecules in the sample with a selected frequency of light. Another vital use is in optical fiber technologies where fibers are designed to provide optimum performance at specific wavelengths. A range of diffraction gratings are available for selecting specific wavelengths for such use.
The spacing of the grooves in a CD or DVD can be well determined by using a laser and the equation . However, we can still make a good estimate of this spacing by using white light and the rainbow of colors that comes from the interference. Reflect sunlight from a CD onto a wall and use your best judgment of the location of a strongly diffracted color to find the separation .
Diffraction gratings with 10,000 lines per centimeter are readily available. Suppose you have one, and you send a beam of white light through it to a screen 2.00 m away. (a) Find the angles for the first-order diffraction of the shortest and longest wavelengths of visible light (380 and 760 nm). (b) What is the distance between the ends of the rainbow of visible light produced on the screen for first-order interference? (See [link] .)
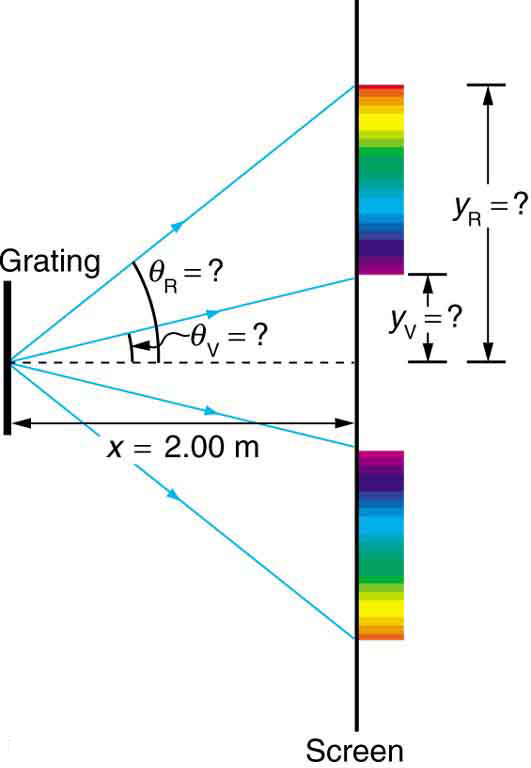
Strategy
The angles can be found using the equation
once a value for the slit spacing has been determined. Since there are 10,000 lines per centimeter, each line is separated by of a centimeter. Once the angles are found, the distances along the screen can be found using simple trigonometry.
Solution for (a)
The distance between slits is or . Let us call the two angles for violet (380 nm) and for red (760 nm). Solving the equation for ,
where for first order and . Substituting these values gives

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?