| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
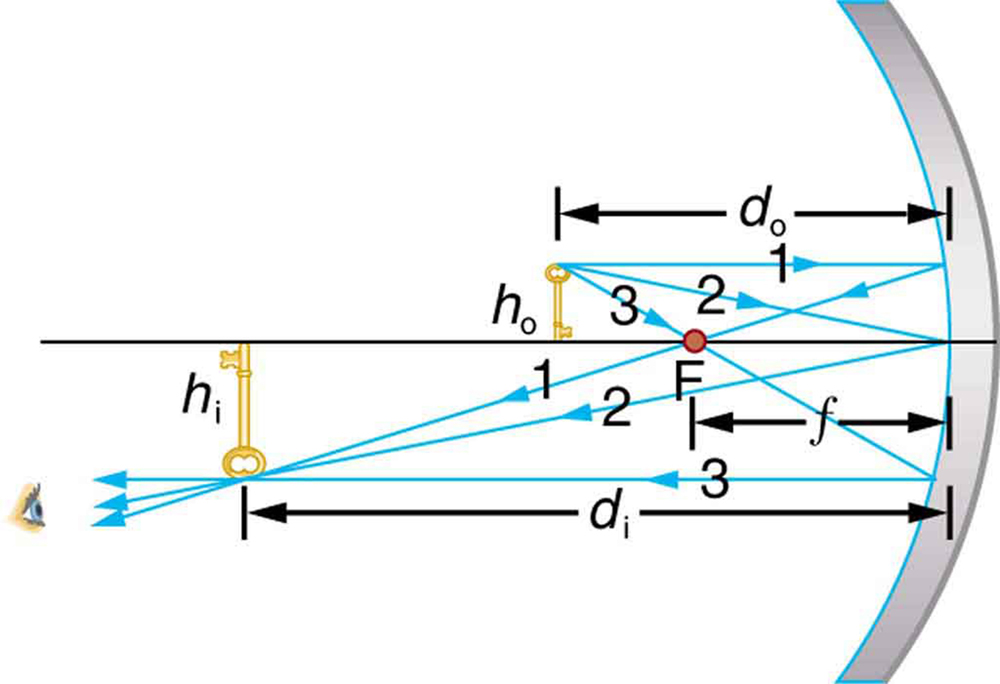
Electric room heaters use a concave mirror to reflect infrared (IR) radiation from hot coils. Note that IR follows the same law of reflection as visible light. Given that the mirror has a radius of curvature of 50.0 cm and produces an image of the coils 3.00 m away from the mirror, where are the coils?
Strategy and Concept
We are given that the concave mirror projects a real image of the coils at an image distance . The coils are the object, and we are asked to find their location—that is, to find the object distance . We are also given the radius of curvature of the mirror, so that its focal length is (positive since the mirror is concave or converging). Assuming the mirror is small compared with its radius of curvature, we can use the thin lens equations, to solve this problem.
Solution
Since and are known, thin lens equation can be used to find :
Rearranging to isolate gives
Entering known quantities gives a value for :
This must be inverted to find :
Discussion
Note that the object (the filament) is farther from the mirror than the mirror’s focal length. This is a case 1 image ( and positive), consistent with the fact that a real image is formed. You will get the most concentrated thermal energy directly in front of the mirror and 3.00 m away from it. Generally, this is not desirable, since it could cause burns. Usually, you want the rays to emerge parallel, and this is accomplished by having the filament at the focal point of the mirror.
Note that the filament here is not much farther from the mirror than its focal length and that the image produced is considerably farther away. This is exactly analogous to a slide projector. Placing a slide only slightly farther away from the projector lens than its focal length produces an image significantly farther away. As the object gets closer to the focal distance, the image gets farther away. In fact, as the object distance approaches the focal length, the image distance approaches infinity and the rays are sent out parallel to one another.
One of the solar technologies used today for generating electricity is a device (called a parabolic trough or concentrating collector) that concentrates the sunlight onto a blackened pipe that contains a fluid. This heated fluid is pumped to a heat exchanger, where its heat energy is transferred to another system that is used to generate steam—and so generate electricity through a conventional steam cycle. [link] shows such a working system in southern California. Concave mirrors are used to concentrate the sunlight onto the pipe. The mirror has the approximate shape of a section of a cylinder. For the problem, assume that the mirror is exactly one-quarter of a full cylinder.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?