| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The second condition necessary to achieve equilibrium involves avoiding accelerated rotation (maintaining a constant angular velocity. A rotating body or system can be in equilibrium if its rate of rotation is constant and remains unchanged by the forces acting on it. To understand what factors affect rotation, let us think about what happens when you open an ordinary door by rotating it on its hinges.
Several familiar factors determine how effective you are in opening the door. See [link] . First of all, the larger the force, the more effective it is in opening the door—obviously, the harder you push, the more rapidly the door opens. Also, the point at which you push is crucial. If you apply your force too close to the hinges, the door will open slowly, if at all. Most people have been embarrassed by making this mistake and bumping up against a door when it did not open as quickly as expected. Finally, the direction in which you push is also important. The most effective direction is perpendicular to the door—we push in this direction almost instinctively.
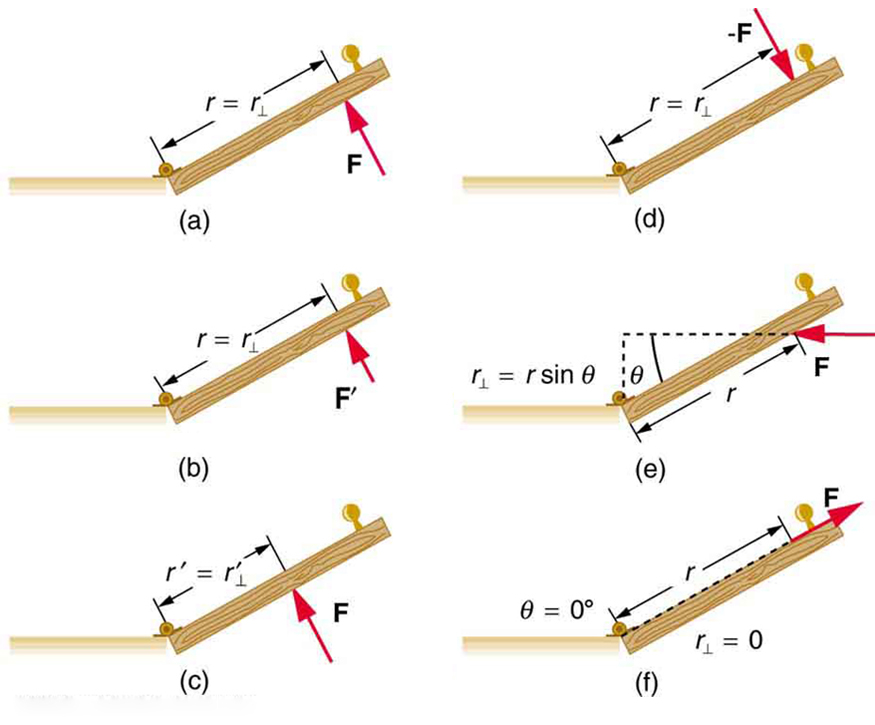
The magnitude, direction, and point of application of the force are incorporated into the definition of the physical quantity called torque. Torque is the rotational equivalent of a force. It is a measure of the effectiveness of a force in changing or accelerating a rotation (changing the angular velocity over a period of time). In equation form, the magnitude of torque is defined to be
where (the Greek letter tau) is the symbol for torque, is the distance from the pivot point to the point where the force is applied, is the magnitude of the force, and is the angle between the force and the vector directed from the point of application to the pivot point, as seen in [link] and [link] . An alternative expression for torque is given in terms of the perpendicular lever arm as shown in [link] and [link] , which is defined as

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?