| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Protons and neutrons are bound inside nuclei, that means energy must be supplied to break them away. The situation is analogous to a marble in a bowl that can roll around but lacks the energy to get over the rim. It is bound inside the bowl (see [link] ). If the marble could get over the rim, it would gain kinetic energy by rolling down outside. However classically, if the marble does not have enough kinetic energy to get over the rim, it remains forever trapped in its well.
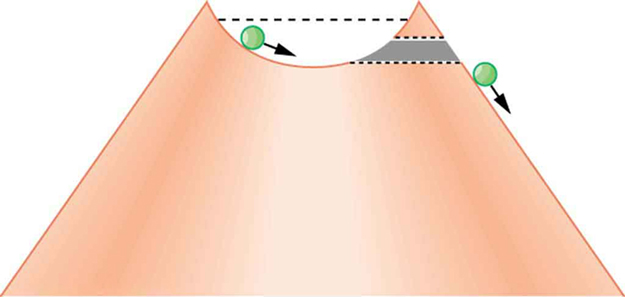
In a nucleus, the attractive nuclear potential is analogous to the bowl at the top of a volcano (where the “volcano” refers only to the shape). Protons and neutrons have kinetic energy, but it is about 8 MeV less than that needed to get out (see [link] ). That is, they are bound by an average of 8 MeV per nucleon. The slope of the hill outside the bowl is analogous to the repulsive Coulomb potential for a nucleus, such as for an particle outside a positive nucleus. In decay, two protons and two neutrons spontaneously break away as a unit. Yet the protons and neutrons do not have enough kinetic energy to get over the rim. So how does the particle get out?
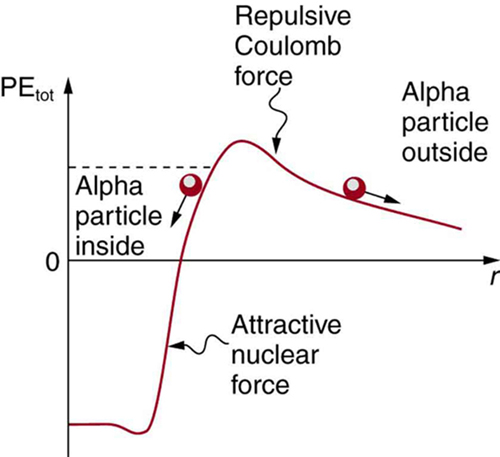
The answer was supplied in 1928 by the Russian physicist George Gamow (1904–1968). The particle tunnels through a region of space it is forbidden to be in, and it comes out of the side of the nucleus. Like an electron making a transition between orbits around an atom, it travels from one point to another without ever having been in between. [link] indicates how this works. The wave function of a quantum mechanical particle varies smoothly, going from within an atomic nucleus (on one side of a potential energy barrier) to outside the nucleus (on the other side of the potential energy barrier). Inside the barrier, the wave function does not become zero but decreases exponentially, and we do not observe the particle inside the barrier. The probability of finding a particle is related to the square of its wave function, and so there is a small probability of finding the particle outside the barrier, which implies that the particle can tunnel through the barrier. This process is called barrier penetration or quantum mechanical tunneling . This concept was developed in theory by J. Robert Oppenheimer (who led the development of the first nuclear bombs during World War II) and was used by Gamow and others to describe decay.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?