| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The bright colors seen in an oil slick floating on water or in a sunlit soap bubble are caused by interference. The brightest colors are those that interfere constructively. This interference is between light reflected from different surfaces of a thin film; thus, the effect is known as thin film interference . As noticed before, interference effects are most prominent when light interacts with something having a size similar to its wavelength. A thin film is one having a thickness smaller than a few times the wavelength of light, . Since color is associated indirectly with and since all interference depends in some way on the ratio of to the size of the object involved, we should expect to see different colors for different thicknesses of a film, as in [link] .
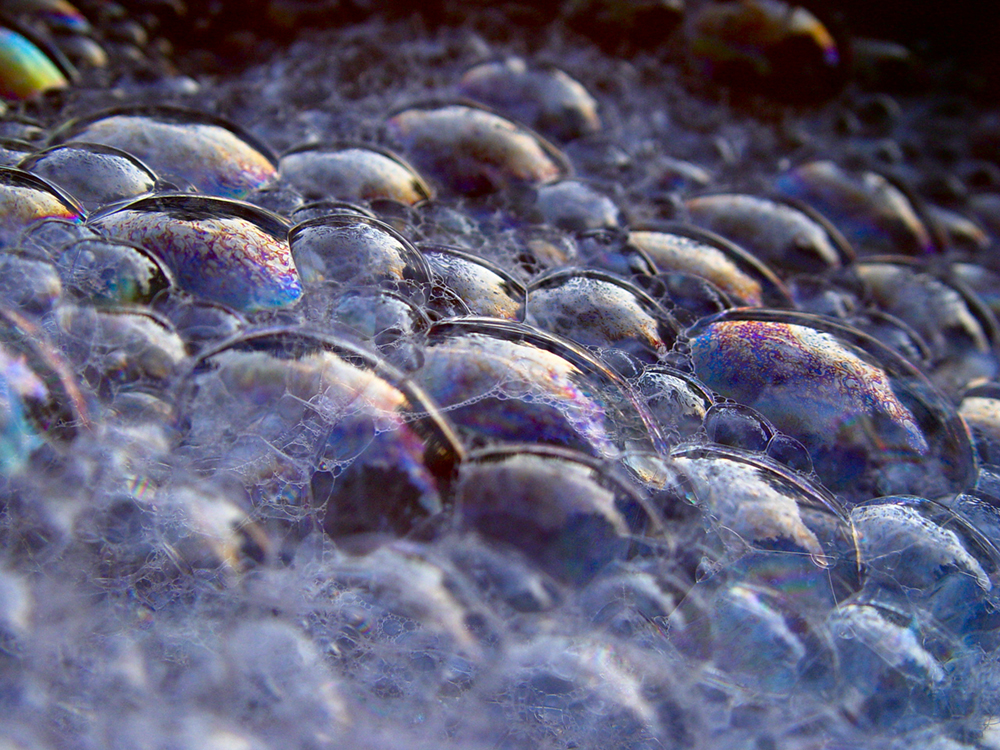

What causes thin film interference? [link] shows how light reflected from the top and bottom surfaces of a film can interfere. Incident light is only partially reflected from the top surface of the film (ray 1). The remainder enters the film and is itself partially reflected from the bottom surface. Part of the light reflected from the bottom surface can emerge from the top of the film (ray 2) and interfere with light reflected from the top (ray 1). Since the ray that enters the film travels a greater distance, it may be in or out of phase with the ray reflected from the top. However, consider for a moment, again, the bubbles in [link] . The bubbles are darkest where they are thinnest. Furthermore, if you observe a soap bubble carefully, you will note it gets dark at the point where it breaks. For very thin films, the difference in path lengths of ray 1 and ray 2 in [link] is negligible; so why should they interfere destructively and not constructively? The answer is that a phase change can occur upon reflection. The rule is as follows:
When light reflects from a medium having an index of refraction greater than that of the medium in which it is traveling, a phase change (or a shift) occurs.
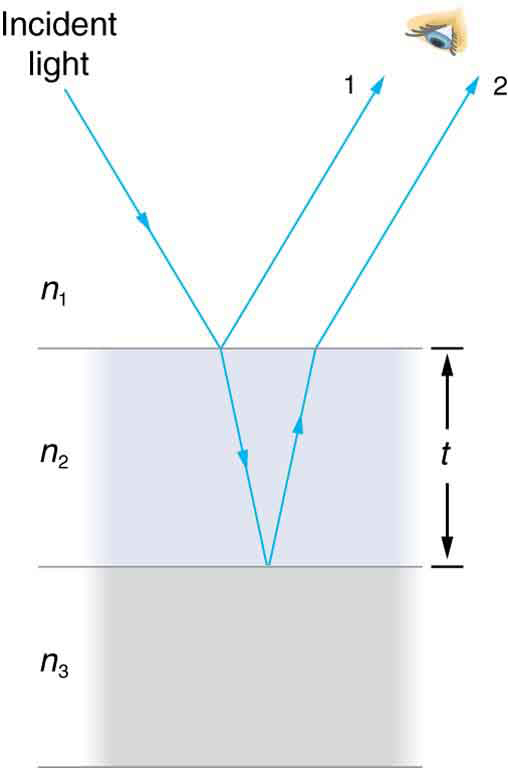
If the film in [link] is a soap bubble (essentially water with air on both sides), then there is a shift for ray 1 and none for ray 2. Thus, when the film is very thin, the path length difference between the two rays is negligible, they are exactly out of phase, and destructive interference will occur at all wavelengths and so the soap bubble will be dark here.
The thickness of the film relative to the wavelength of light is the other crucial factor in thin film interference. Ray 2 in [link] travels a greater distance than ray 1. For light incident perpendicular to the surface, ray 2 travels a distance approximately farther than ray 1. When this distance is an integral or half-integral multiple of the wavelength in the medium ( , where is the wavelength in vacuum and is the index of refraction), constructive or destructive interference occurs, depending also on whether there is a phase change in either ray.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?