| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We can get a good understanding of electromagnetic waves (EM) by considering how they are produced. Whenever a current varies, associated electric and magnetic fields vary, moving out from the source like waves. Perhaps the easiest situation to visualize is a varying current in a long straight wire, produced by an AC generator at its center, as illustrated in [link] .
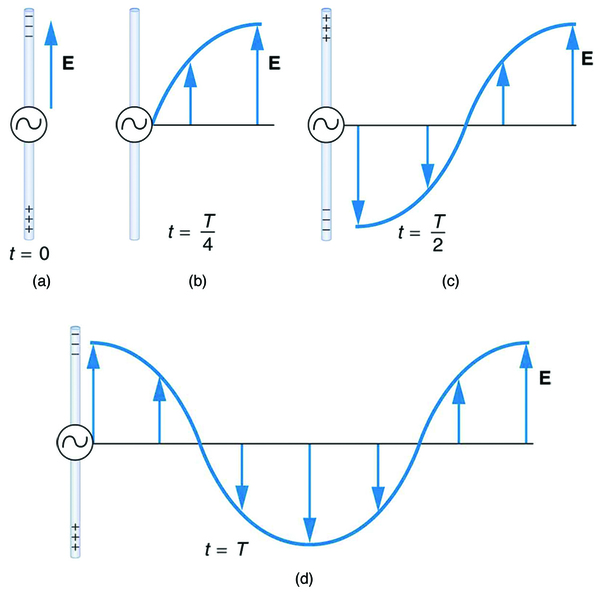
The electric field ( ) shown surrounding the wire is produced by the charge distribution on the wire. Both the and the charge distribution vary as the current changes. The changing field propagates outward at the speed of light.
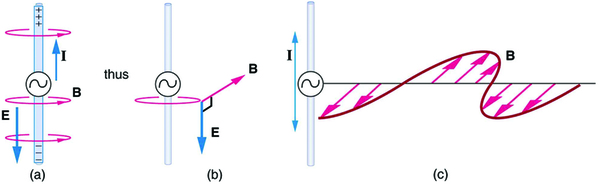
There is an associated magnetic field ( ) which propagates outward as well (see [link] ). The electric and magnetic fields are closely related and propagate as an electromagnetic wave. This is what happens in broadcast antennae such as those in radio and TV stations.
Closer examination of the one complete cycle shown in [link] reveals the periodic nature of the generator-driven charges oscillating up and down in the antenna and the electric field produced. At time , there is the maximum separation of charge, with negative charges at the top and positive charges at the bottom, producing the maximum magnitude of the electric field (or -field) in the upward direction. One-fourth of a cycle later, there is no charge separation and the field next to the antenna is zero, while the maximum -field has moved away at speed .
As the process continues, the charge separation reverses and the field reaches its maximum downward value, returns to zero, and rises to its maximum upward value at the end of one complete cycle. The outgoing wave has an amplitude proportional to the maximum separation of charge. Its wavelength is proportional to the period of the oscillation and, hence, is smaller for short periods or high frequencies. (As usual, wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional.)
Following Ampere’s law, current in the antenna produces a magnetic field, as shown in [link] . The relationship between and is shown at one instant in [link] (a). As the current varies, the magnetic field varies in magnitude and direction.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?