| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

Interference is the hallmark of waves, all of which exhibit constructive and destructive interference exactly analogous to that seen for water waves. In fact, one way to prove something “is a wave” is to observe interference effects. So, sound being a wave, we expect it to exhibit interference; we have already mentioned a few such effects, such as the beats from two similar notes played simultaneously.
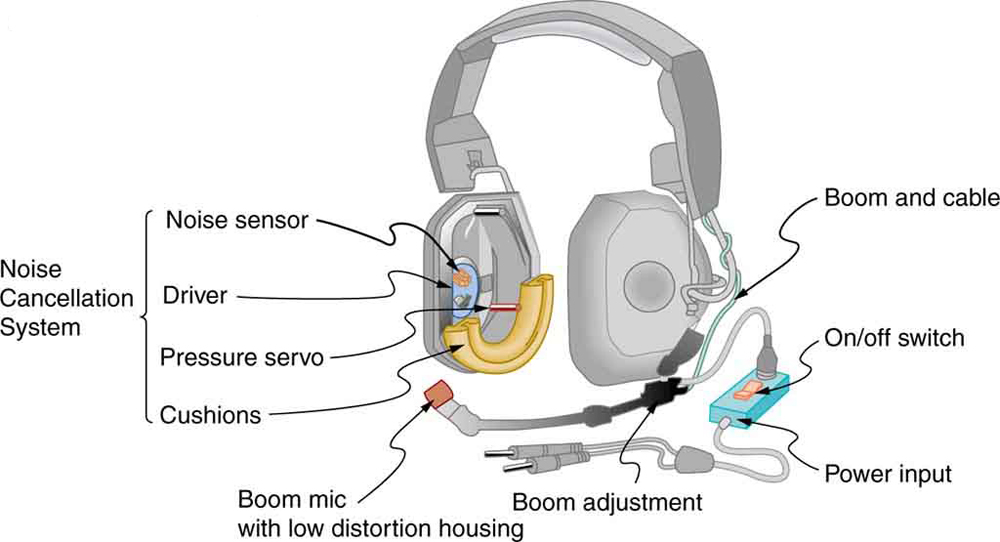
[link] shows a clever use of sound interference to cancel noise. Larger-scale applications of active noise reduction by destructive interference are contemplated for entire passenger compartments in commercial aircraft. To obtain destructive interference, a fast electronic analysis is performed, and a second sound is introduced with its maxima and minima exactly reversed from the incoming noise. Sound waves in fluids are pressure waves and consistent with Pascal’s principle; pressures from two different sources add and subtract like simple numbers; that is, positive and negative gauge pressures add to a much smaller pressure, producing a lower-intensity sound. Although completely destructive interference is possible only under the simplest conditions, it is possible to reduce noise levels by 30 dB or more using this technique.
Where else can we observe sound interference? All sound resonances, such as in musical instruments, are due to constructive and destructive interference. Only the resonant frequencies interfere constructively to form standing waves, while others interfere destructively and are absent. From the toot made by blowing over a bottle, to the characteristic flavor of a violin’s sounding box, to the recognizability of a great singer’s voice, resonance and standing waves play a vital role.
Interference is such a fundamental aspect of waves that observing interference is proof that something is a wave. The wave nature of light was established by experiments showing interference. Similarly, when electrons scattered from crystals exhibited interference, their wave nature was confirmed to be exactly as predicted by symmetry with certain wave characteristics of light.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?