| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
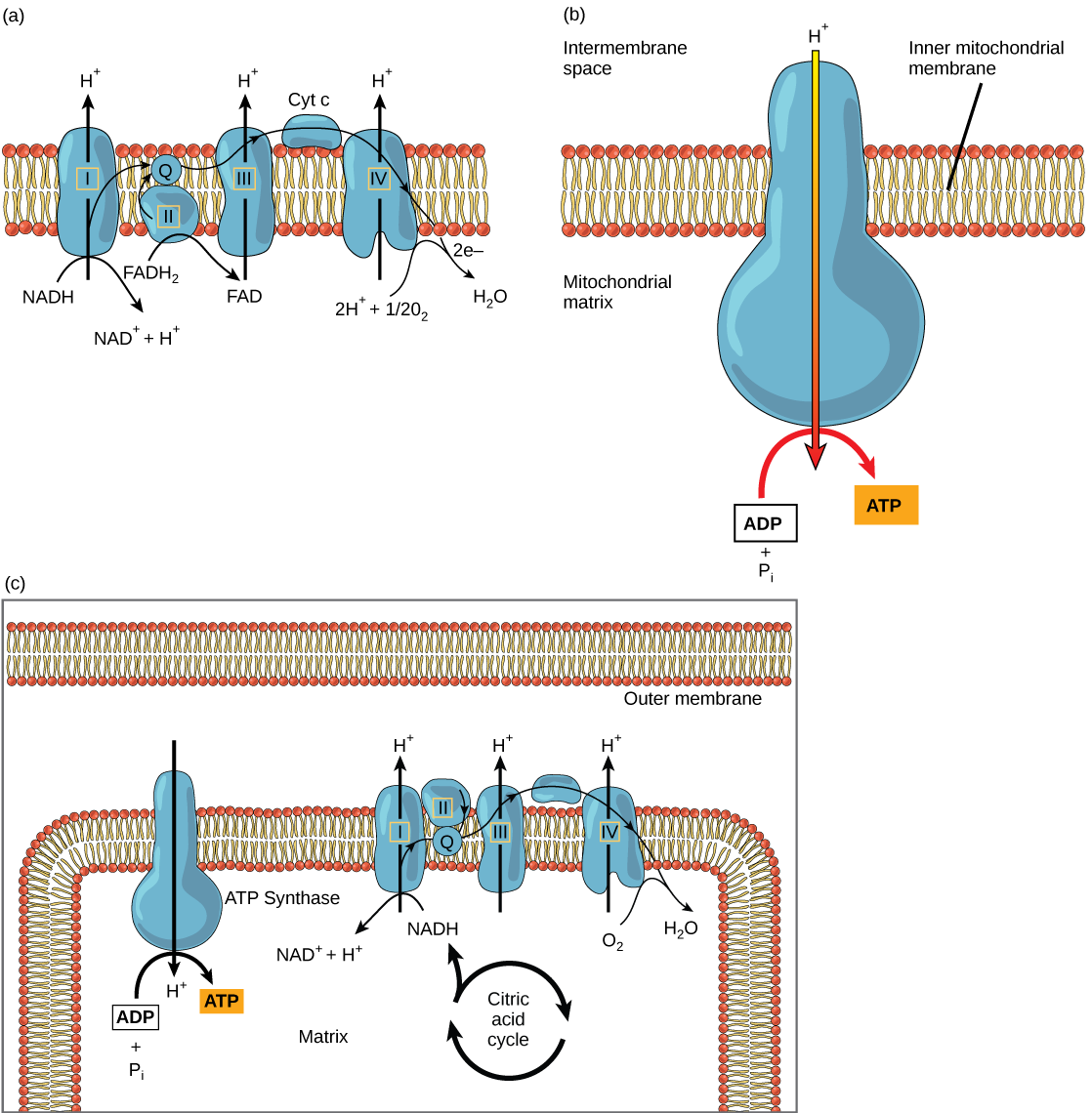
The electron transport chain ( [link] a ) is the last component of aerobic respiration and is the only part of metabolism that uses atmospheric oxygen. Oxygen continuously diffuses into plants for this purpose. In animals, oxygen enters the body through the respiratory system. Electron transport is a series of chemical reactions that resembles a bucket brigade in that electrons are passed rapidly from one component to the next, to the endpoint of the chain where oxygen is the final electron acceptor and water is produced. There are four complexes composed of proteins, labeled I through IV in [link] c , and the aggregation of these four complexes, together with associated mobile, accessory electron carriers, is called the electron transport chain . The electron transport chain is present in multiple copies in the inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotes and in the plasma membrane of prokaryotes. In each transfer of an electron through the electron transport chain, the electron loses energy, but with some transfers, the energy is stored as potential energy by using it to pump hydrogen ions across the inner mitochondrial membrane into the intermembrane space, creating an electrochemical gradient.
Cyanide inhibits cytochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain. If cyanide poisoning occurs, would you expect the pH of the intermembrane space to increase or decrease? What affect would cyanide have on ATP synthesis?
Electrons from NADH and FADH 2 are passed to protein complexes in the electron transport chain. As they are passed from one complex to another (there are a total of four), the electrons lose energy, and some of that energy is used to pump hydrogen ions from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space. In the fourth protein complex, the electrons are accepted by oxygen, the terminal acceptor. The oxygen with its extra electrons then combines with two hydrogen ions, further enhancing the electrochemical gradient, to form water. If there were no oxygen present in the mitochondrion, the electrons could not be removed from the system, and the entire electron transport chain would back up and stop. The mitochondria would be unable to generate new ATP in this way, and the cell would ultimately die from lack of energy. This is the reason we must breathe to draw in new oxygen.
In the electron transport chain, the energy from the series of reactions just described is used to pump hydrogen ions across the membrane. The uneven distribution of H + ions across the membrane establishes an electrochemical gradient, owing to the H + ions’ positive charge and their higher concentration on one side of the membrane.
Hydrogen ions diffuse through the inner membrane through an integral membrane protein called ATP synthase ( [link] b ). This complex protein acts as a tiny generator, turned by the force of the hydrogen ions diffusing through it, down their electrochemical gradient from the intermembrane space, where there are many mutually repelling hydrogen ions to the matrix, where there are few. The turning of the parts of this molecular machine regenerate ATP from ADP. This flow of hydrogen ions across the membrane through ATP synthase is called chemiosmosis .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'General biology part i - mixed majors' conversation and receive update notifications?