| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We have examined several versions of the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus in higher dimensions that relate the integral around an oriented boundary of a domain to a “derivative” of that entity on the oriented domain. In this section, we state the divergence theorem, which is the final theorem of this type that we will study. The divergence theorem has many uses in physics; in particular, the divergence theorem is used in the field of partial differential equations to derive equations modeling heat flow and conservation of mass. We use the theorem to calculate flux integrals and apply it to electrostatic fields.
Before examining the divergence theorem, it is helpful to begin with an overview of the versions of the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus we have discussed:
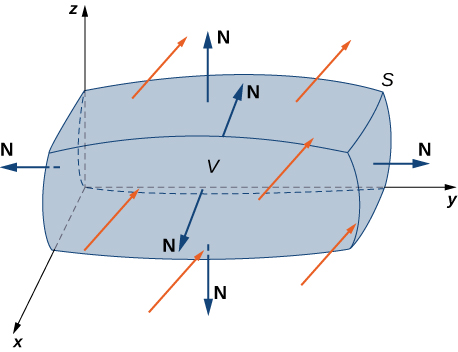
The divergence theorem follows the general pattern of these other theorems. If we think of divergence as a derivative of sorts, then the divergence theorem relates a triple integral of derivative div F over a solid to a flux integral of F over the boundary of the solid. More specifically, the divergence theorem relates a flux integral of vector field F over a closed surface S to a triple integral of the divergence of F over the solid enclosed by S .
Let S be a piecewise, smooth closed surface that encloses solid E in space. Assume that S is oriented outward, and let F be a vector field with continuous partial derivatives on an open region containing E ( [link] ). Then

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?