| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
ACTIVITY 4
To tell expressions and equations apart
[LO 2.1, 2.6]
ACTIVITY 5
To solve two equations simultaneously
[LO 2.4, 2.9]
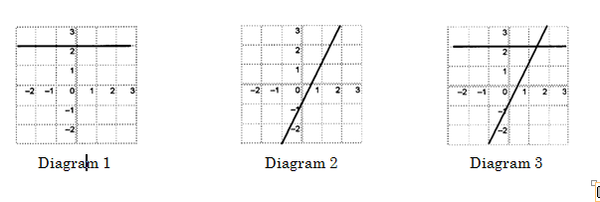
1. The line in figure 1 has defining equation y = 2.
Question: Does the point (1 ; 1) lie on the line?
Answer: We can obtain the answer graphically (by looking at the graph). So we can see that the point does not lie on the line, making the answer no .
We can obtain the answer algebraically , as follows: Substitute the point (1 ; 1) for ( x ; y ) in the equation. Do the LHS and RHS separately as before.
LHS: y = ( 1 ) = 2 RHS: 2 LHS ≠ RHS – the point (1 ; 1) does not lie on y = 2.
Question: Does the point (–2 ; 2) lie on the line?
Graphically : Yes.
Algebraically : LHS: y = ( 2 ) = 2 RHS: 2 LHS = RHS; yes it does.
Question: Does the point (1½ ; 2) lie on the line? Find the answer both graphically and algebraically.
2. The line in figure 2 is defined by the equation y = 2 x – 1.
Questions: Does the point (0 ; 0) lie on the line?
Does the point (1 ; 1) lie on y = 2 x – 1?
Does the point (1½ ; 2) lie on the line?
3. In figure 3 the same two lines are drawn together on the same set of axes.
Answer graphically: Which point lies on both lines? The answers to questions 1 and 2 above will be helpful.
It is easy to see from the graph that the only point that lies on both lines is (1½ ; 2).
From the line y = 2 we can see that y has the value 2. If we substitute this value into the equation y = 2 x – 1.
We can solve the equation to get a value for x . So:
Substitute: ( 2 ) = 2 x – 1 and solve for x :
2 = 2 x – 1 now move the x –terms to the left
–2 x + 2 = –1 now move the constant terms to the right
–2 x = –2 – 1 simplify
–2 x = –3 divide both sides by –2
x = –3 –2 simplify
x = 1½
This shows that the point where the lines cross is ( x ; y ) = (1½ ; 2).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 9' conversation and receive update notifications?