| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
DIFFERENCES
between rhombus and square
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
17.2 From other groups of three. Follow the same instructions as for 17.1 but build a rectangle instead. If you press on a corner it will change into a parallelogram.
SIMILARITIES
between rectangle and parallelogram
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
DIFFERENCES
between rectangle and parallelogram
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
18. What do we call this geometric figure?
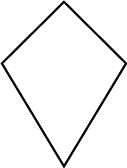
__________________________________________
b)
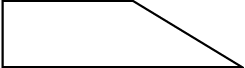
__________________________________________
19. Form groups of four. Your teacher will say who must do a, b, c, and d.
19.1 Discuss the similarities and differences between:
a) a rhombus and a kite;
b) a trapezium and a parallelogram;
c) a rectangle and a trapezium;
d) a kite and a trapezium.
19.2 Make a poster to explain the above and report back to the class.
20. Did you know?
In maths we say a figure / structure is rigid if it can keep its original form even though pressure is applied to one of its corners, e.g.
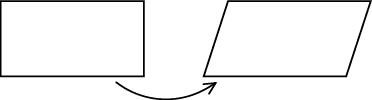
Not sturdy
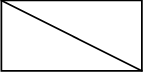
Sturdy
20.1 Divide into pairs. Use cool drink straws and build any rigid structure. See if you can build the highest structure in the class!
20.2 TAKE NOTE!
A triangle is the only polygon that is rigid. It doesn’t change its form when pressure is applied to any of its corners.
Where, do you think, do engineers and builders regularly use triangles to ensure stability in their constructions?
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
21. Time for self-assessment
|
Uncertain | Certain |
| I can explain what the following are: | ||
|
___ | ___ |
|
___ | ___ |
|
___ | ___ |
|
___ | ___ |
|
___ | ___ |
| I know the formula to determine / calculate the size of the angles of a regular polygon | ___ | ___ |
| I can point out the similarities between different geometric forms. | ___ | ___ |
| I can point out the differences between different geometric forms. | ___ | ___ |
| I can build a rigid construction with cool drink straws | ___ | ___ |
Learning Outcome 3: The learner will be able to describe and represent characteristics and relationships between two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional objects in a variety of orientations and positions.
Assessment Standard 3.1: We know this when the learner recognises, visualises and names geometric figures and solids in natural and cultural forms and geometric settings, including those previously dealt with.
Learning Outcome 2: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent patterns and relationships, as well as to solve problems using algebraic language and skills.
Assessment Standard 2.3: We know this when the learner represents and uses relationships between variables in order to determine input and/or output values in a variety of ways.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 7' conversation and receive update notifications?