| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Now that we have a formal method---the node method---for solving circuits, we can use it to prove a powerful result: KVL and KCL are all that are required to show that all circuits conserve power, regardless of what elements are used to build the circuit.
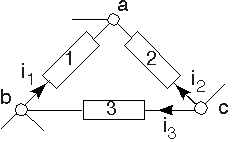
First of all, define node voltages for all nodes in a given circuit. Any node chosen as the reference will do.For example, in the portion of a large circuit depicted here, we define node voltages for nodes a, b and c. With these node voltages, we can express the voltage across any element in terms of them.For example, the voltage across element 1 is given by . The instantaneous power for element 1 becomes Writing the power for the other elements, we have When we add together the element power terms, we discover that once we collect terms involving a particular node voltage, it is multiplied by the sum of currents leaving the node minus the sum of currents entering. For example, for node b, we have . We see that the currents will obey KCL that multiply each node voltage.Consequently, we conclude that the sum of element powers must equal zero in any circuit regardless of the elements used to construct the circuit .
The simplicity and generality with which we proved this results generalizes to other situations as well. In particular, note that the complex amplitudes of voltages and currents obey KVL and KCL, respectively.Consequently, we have that . Furthermore, the complex-conjugate of currents also satisfies KCL, which means we also have . And finally, we know that evaluating the real-part of an expression is linear.Finding the real-part of this power conservation gives the result that average power is also conserved in any circuit .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Fundamentals of electrical engineering i' conversation and receive update notifications?