| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
1. The topography of South Africa
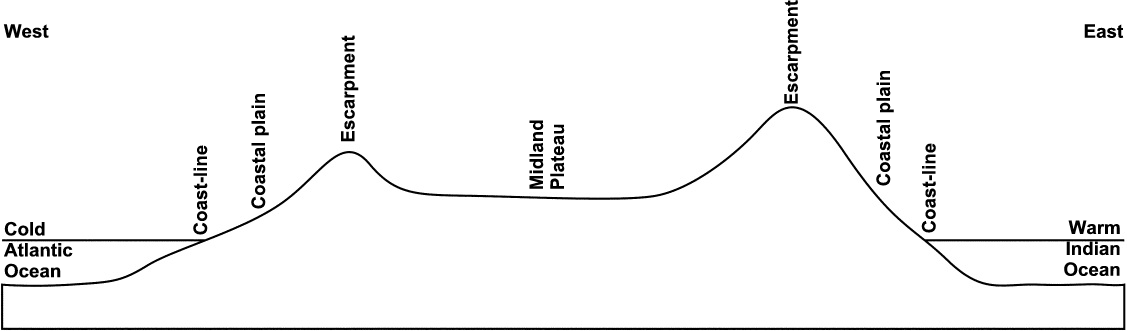
Figure 1: A cross-profile of the RSA
2. Factors affecting South Africa’s climate
T emperature
South Africa displays typical temperature patterns during different seasons. Few people plan a holiday on the west coast in winter, while Durban (south-east coast) has ideal holiday temperatures during winter.
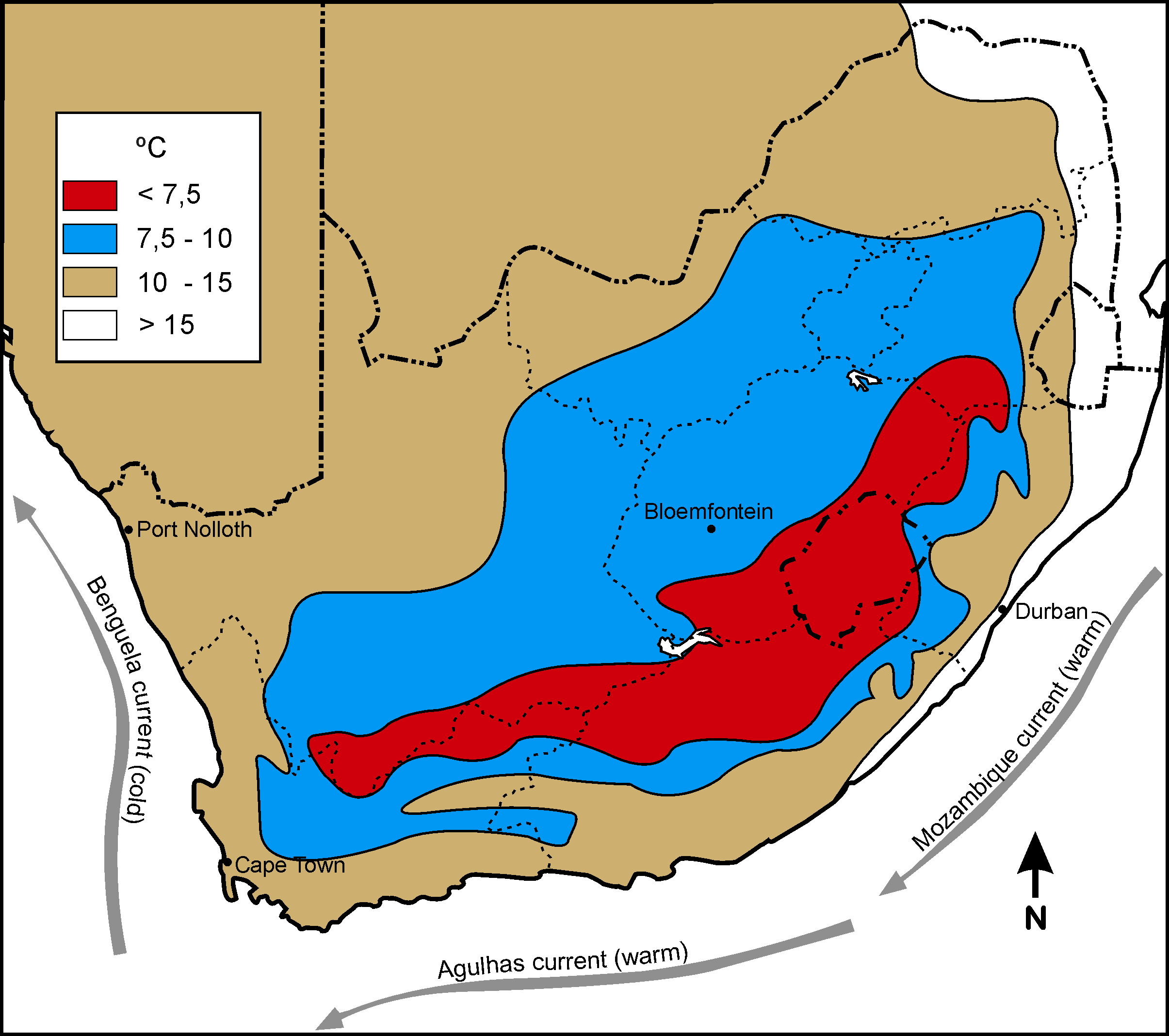 |
| Winter temperature in South Africa |
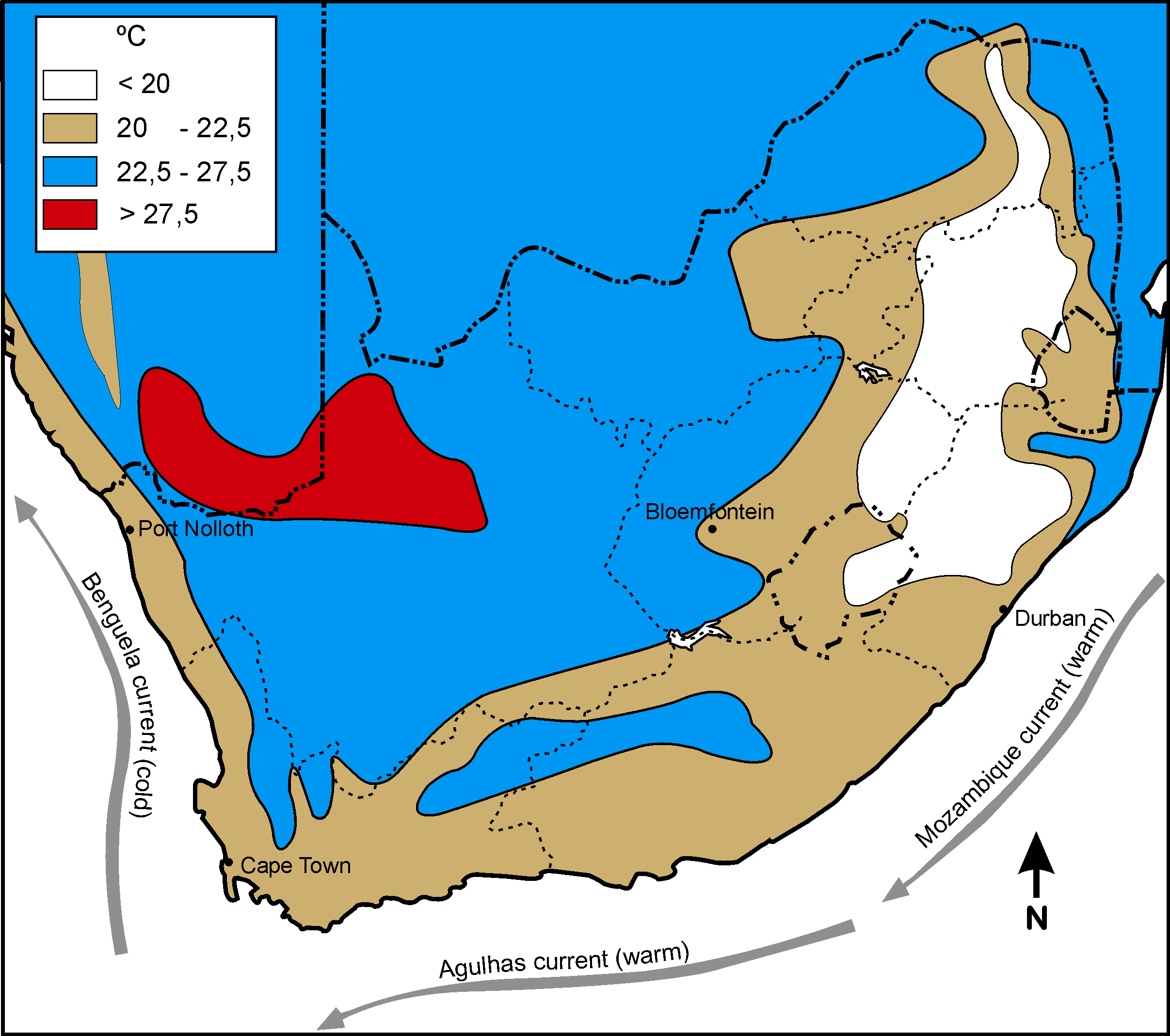 |
| Summer temperature in South Africa |
The temperature of the RSA is influenced by the following:
Latitude location
The further a region is located from the Equator (0º L), the colder it is. Places in the tropics therefore experience warmer temperatures than places at the poles.
Altitude
The higher you go above sea level, the colder it becomes. Temperature therefore drops as altitude increases. Because the RSA’s interior plateau is located high above sea level, it will be colder there than in parts along lower coastal areas. Frost is common on the interior plateau and snow occurs on the high mountains.
Sea currents
The warm Mozambique current flows southwest along the RSA’s east coast, and the cold Benguela current flows north along the west coast. Air above a cold current is cold and there is little chance of rain. With a warm current the air is warm, rises, condenses and clouds and rain occur.
Distance from the sea
The sea has a moderating effect on climate. This means that areas that are close to the sea are not too hot in summer and not too cold in winter. The temperature margin is therefore small (difference between the highest and lowest temperatures). The reason for this is that water masses are not heated as quickly through insulation as the land surfaces. However, once water has absorbed heat, it retains it for longer than land surfaces. During the day radiation of heat from the soil is high, but it is low at night.
During the day the radiation from the sea’s water is less and this results in lower temperatures than in the case of the interior. At night the earth radiates heat for longer and the coastal areas are therefore warmer at night than the interior. Use this information to do the following activities.
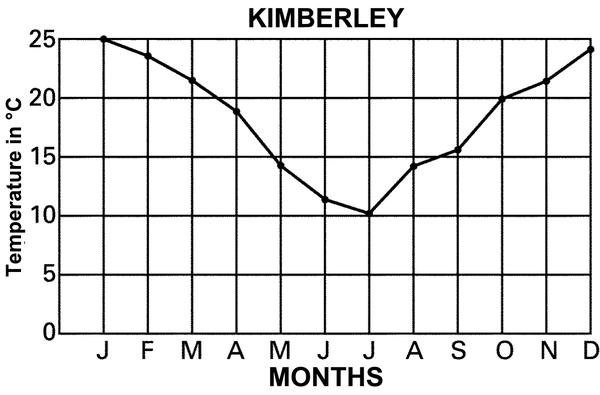
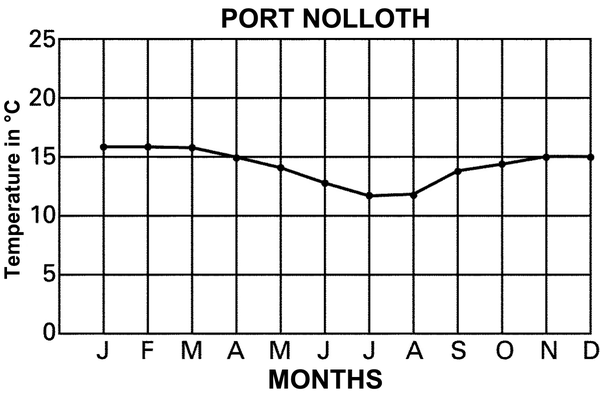
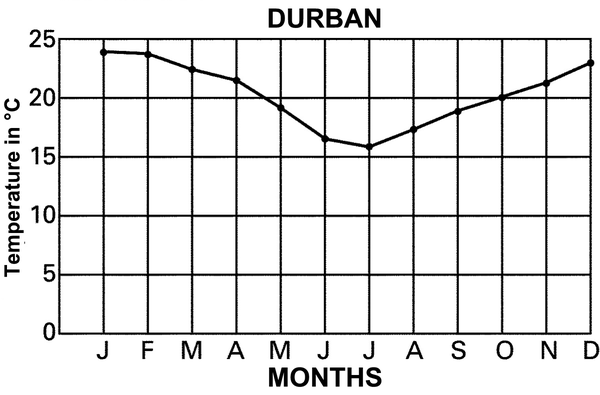
Explain why the day and night temperatures in Kimberley differ much more than those in Port Nolloth and Durban.
Why is Durban’s temperature higher than that of Port Nolloth? Use your atlas to find the places if you are unsure.
Study the following temperatures. Find the location of the various places in an atlas if you do not know where they are located. Remember the labels and headings.
| Months | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sept | Oct | Nov | Dec |
| Bloem-fontein24°S;1 400 mabove sea level | 23 | 22 | 20 | 16 | 11 | 9 | 8 | 11 | 15 | 18 | 20 | 22 |
| Cape Town34°S; sea level | 22 | 22 | 20 | 18 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 17 | 19 | 20 |
For each place in the above table indicate the following:
Explain the difference in temperature between the following places by referring to the factors that affect the climate of South Africa
LO 1
GEOGRAPHICAL ENQUIRY
The learner will be able to use enquiry skills to investigate geographical and environmental concepts and processes.
We know this when the learner:
1.1 with guidance, selects and uses sources of useful geographical information (including graphs, maps and fieldwork outside the classroom) [finds sources];
1.7 demonstrates knowledge and under-standing of the issue through projects, discussion, debate and charts [communicates the answer].

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Social sciences: geography grade 5' conversation and receive update notifications?