| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Coronary veins drain the heart and generally parallel the large surface arteries (see [link] ). The great cardiac vein can be seen initially on the surface of the heart following the interventricular sulcus, but it eventually flows along the coronary sulcus into the coronary sinus on the posterior surface. The great cardiac vein initially parallels the anterior interventricular artery and drains the areas supplied by this vessel. It receives several major branches, including the posterior cardiac vein, the middle cardiac vein, and the small cardiac vein. The posterior cardiac vein parallels and drains the areas supplied by the marginal artery branch of the circumflex artery. The middle cardiac vein parallels and drains the areas supplied by the posterior interventricular artery. The small cardiac vein parallels the right coronary artery and drains the blood from the posterior surfaces of the right atrium and ventricle. The coronary sinus is a large, thin-walled vein on the posterior surface of the heart lying within the atrioventricular sulcus and emptying directly into the right atrium. The anterior cardiac veins parallel the small cardiac arteries and drain the anterior surface of the right ventricle. Unlike these other cardiac veins, it bypasses the coronary sinus and drains directly into the right atrium.
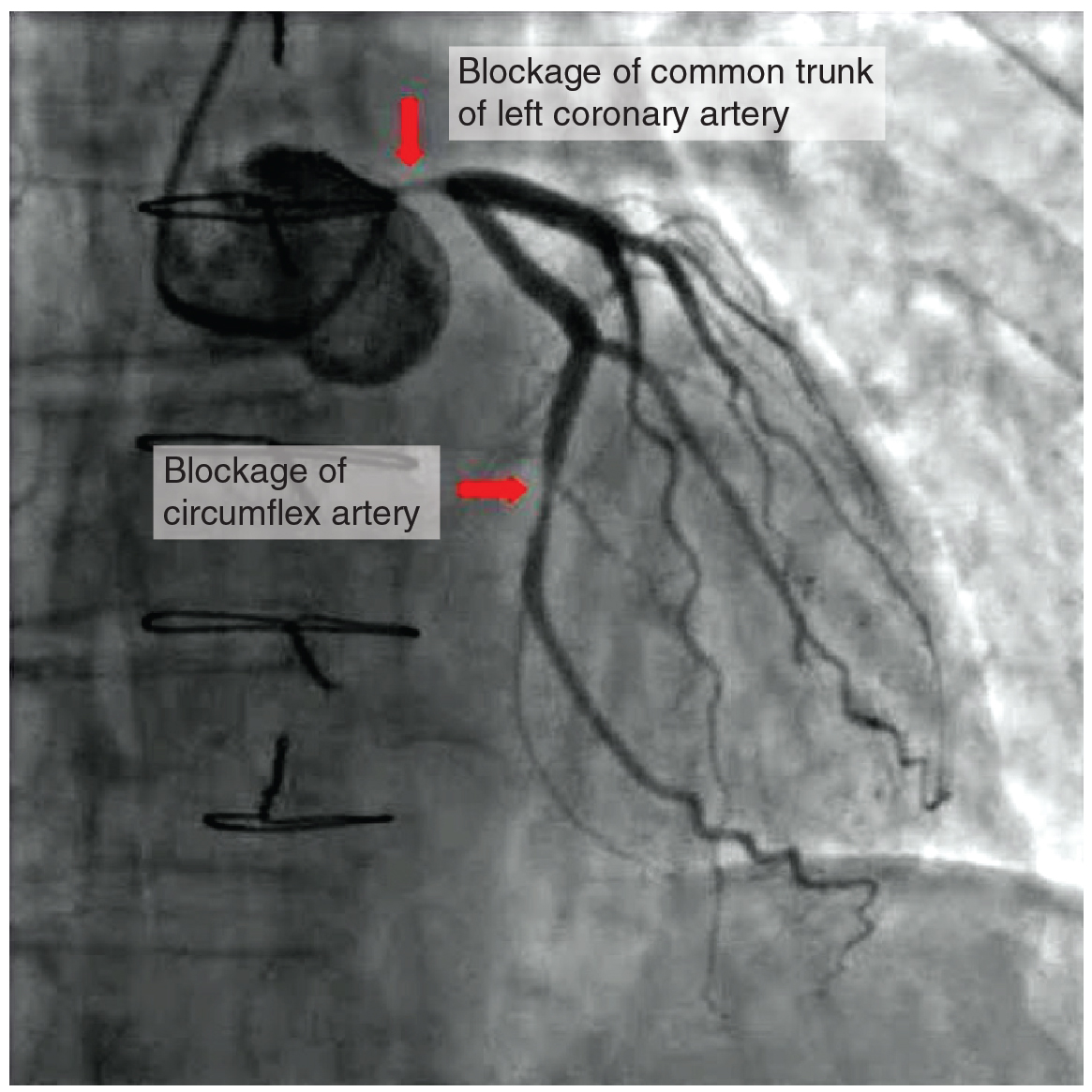
Coronary artery disease is the leading cause of death worldwide. It occurs when the buildup of plaque—a fatty material including cholesterol, connective tissue, white blood cells, and some smooth muscle cells—within the walls of the arteries obstructs the flow of blood and decreases the flexibility or compliance of the vessels. This condition is called atherosclerosis, a hardening of the arteries that involves the accumulation of plaque. As the coronary blood vessels become occluded, the flow of blood to the tissues will be restricted, a condition called ischemia that causes the cells to receive insufficient amounts of oxygen, called hypoxia. [link] shows the blockage of coronary arteries highlighted by the injection of dye. Some individuals with coronary artery disease report pain radiating from the chest called angina pectoris, but others remain asymptomatic. If untreated, coronary artery disease can lead to MI or a heart attack.
The disease progresses slowly and often begins in children and can be seen as fatty “streaks” in the vessels. It then gradually progresses throughout life. Well-documented risk factors include smoking, family history, hypertension, obesity, diabetes, high alcohol consumption, lack of exercise, stress, and hyperlipidemia or high circulating levels of lipids in the blood. Treatments may include medication, changes to diet and exercise, angioplasty with a balloon catheter, insertion of a stent, or coronary bypass procedure.
Angioplasty is a procedure in which the occlusion is mechanically widened with a balloon. A specialized catheter with an expandable tip is inserted into a superficial vessel, normally in the leg, and then directed to the site of the occlusion. At this point, the balloon is inflated to compress the plaque material and to open the vessel to increase blood flow. Then, the balloon is deflated and retracted. A stent consisting of a specialized mesh is typically inserted at the site of occlusion to reinforce the weakened and damaged walls. Stent insertions have been routine in cardiology for more than 40 years.
Coronary bypass surgery may also be performed. This surgical procedure grafts a replacement vessel obtained from another, less vital portion of the body to bypass the occluded area. This procedure is clearly effective in treating patients experiencing a MI, but overall does not increase longevity. Nor does it seem advisable in patients with stable although diminished cardiac capacity since frequently loss of mental acuity occurs following the procedure. Long-term changes to behavior, emphasizing diet and exercise plus a medicine regime tailored to lower blood pressure, lower cholesterol and lipids, and reduce clotting are equally as effective.
The heart resides within the pericardial sac and is located in the mediastinal space within the thoracic cavity. The pericardial sac consists of two fused layers: an outer fibrous capsule and an inner parietal pericardium lined with a serous membrane. Between the pericardial sac and the heart is the pericardial cavity, which is filled with lubricating serous fluid. The walls of the heart are composed of an outer epicardium, a thick myocardium, and an inner lining layer of endocardium. The human heart consists of a pair of atria, which receive blood and pump it into a pair of ventricles, which pump blood into the vessels. The right atrium receives systemic blood relatively low in oxygen and pumps it into the right ventricle, which pumps it into the pulmonary circuit. Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs in the lungs, and blood high in oxygen returns to the left atrium, which pumps blood into the left ventricle, which in turn pumps blood into the aorta and the remainder of the systemic circuit. The septa are the partitions that separate the chambers of the heart. They include the interatrial septum, the interventricular septum, and the atrioventricular septum. Two of these openings are guarded by the atrioventricular valves, the right tricuspid valve and the left mitral valve, which prevent the backflow of blood. Each is attached to chordae tendineae that extend to the papillary muscles, which are extensions of the myocardium, to prevent the valves from being blown back into the atria. The pulmonary valve is located at the base of the pulmonary trunk, and the left semilunar valve is located at the base of the aorta. The right and left coronary arteries are the first to branch off the aorta and arise from two of the three sinuses located near the base of the aorta and are generally located in the sulci. Cardiac veins parallel the small cardiac arteries and generally drain into the coronary sinus.
Visit this site to observe an echocardiogram of actual heart valves opening and closing. Although much of the heart has been “removed” from this gif loop so the chordae tendineae are not visible, why is their presence more critical for the atrioventricular valves (tricuspid and mitral) than the semilunar (aortic and pulmonary) valves?
The pressure gradient between the atria and the ventricles is much greater than that between the ventricles and the pulmonary trunk and aorta. Without the presence of the chordae tendineae and papillary muscles, the valves would be blown back (prolapsed) into the atria and blood would regurgitate.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the '101-321-va - vertebrate form and function ii' conversation and receive update notifications?