| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Notice that the only factors of 7 are 1 and 7 itself, and that the only factors of 23 are 1 and 23 itself.
The first seven prime numbers are
2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and 17
The number 1 is not considered to be a prime number, and the number 2 is the first and only even prime number.
Many numbers have factors other than themselves and 1. For example, the factors of 28 are 1, 2, 4, 7, 14, and 28 (since each of these whole numbers and only these whole numbers divide into 28 without a remainder).
Prime numbers are very important in the study of mathematics. We will use them soon in our study of fractions. We will now, however, be introduced to an important mathematical principle.
Find the prime factorization of 10.
Both 2 and 5 are prime numbers. Thus,
is the prime factorization of 10.
Find the prime factorization of 60.
The numbers 2, 3, and 5 are all primes. Thus,
is the prime factorization of 60.
Find the prime factorization of 11.
11 is a prime number. Prime factorization applies only to composite numbers.
The following method provides a way of finding the prime factorization of a whole number. The examples that follow will use the method and make it more clear.
Find the prime factorization of 60.
Since 60 is an even number, it is divisible by 2. We will repeatedly divide by 2 until we no longer can (when we start getting a remainder). We shall divide in the following way.
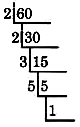
The prime factorization of 60 is the product of all these divisors.
Find the prime factorization of 441.
Since 441 is an odd number, it is not divisible by 2. We’ll try 3, the next largest prime.
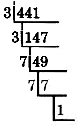
The prime factorization of 441 is the product of all the divisors.
For the following problems, determine which whole numbers are prime and which are composite.
For the following problems, find the prime factorization of each whole number. Use exponents on repeated factors.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Elementary algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?