| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Cell-surface receptors are involved in most of the signaling in multicellular organisms. There are three general categories of cell-surface receptors: ion channel-linked receptors, G-protein-linked receptors, and enzyme-linked receptors.
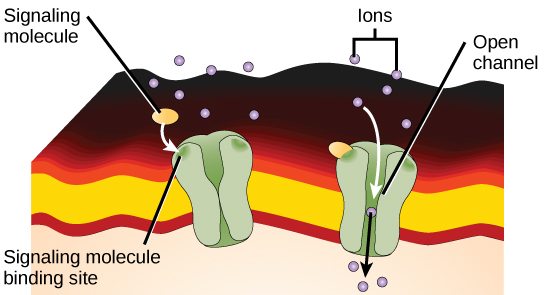
Ion channel-linked receptors bind a ligand and open a channel through the membrane that allows specific ions to pass through. To form a channel, this type of cell-surface receptor has an extensive membrane-spanning region. In order to interact with the phospholipid fatty acid tails that form the center of the plasma membrane, many of the amino acids in the membrane-spanning region are hydrophobic in nature. Conversely, the amino acids that line the inside of the channel are hydrophilic to allow for the passage of water or ions. When a ligand binds to the extracellular region of the channel, there is a conformational change in the proteins structure that allows ions such as sodium, calcium, magnesium, and hydrogen to pass through ( [link] ).
G-protein-linked receptors bind a ligand and activate a membrane protein called a G-protein. The activated G-protein then interacts with either an ion channel or an enzyme in the membrane ( [link] ). All G-protein-linked receptors have seven transmembrane domains, but each receptor has its own specific extracellular domain and G-protein-binding site.
Cell signaling using G-protein-linked receptors occurs as a cyclic series of events. Before the ligand binds, the inactive G-protein can bind to a newly revealed site on the receptor specific for its binding. Once the G-protein binds to the receptor, the resultant shape change activates the G-protein, which releases GDP and picks up GTP. The subunits of the G-protein then split into the α subunit and the βγ subunit. One or both of these G-protein fragments may be able to activate other proteins as a result. After awhile, the GTP on the active α subunit of the G-protein is hydrolyzed to GDP and the βγ subunit is deactivated. The subunits reassociate to form the inactive G-protein and the cycle begins anew.

G-protein-linked receptors have been extensively studied and much has been learned about their roles in maintaining health. Bacteria that are pathogenic to humans can release poisons that interrupt specific G-protein-linked receptor function, leading to illnesses such as pertussis, botulism, and cholera. In cholera ( [link] ), for example, the water-borne bacterium Vibrio cholerae produces a toxin, choleragen, that binds to cells lining the small intestine. The toxin then enters these intestinal cells, where it modifies a G-protein that controls the opening of a chloride channel and causes it to remain continuously active, resulting in large losses of fluids from the body and potentially fatal dehydration as a result.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Genetics and evolution' conversation and receive update notifications?