| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
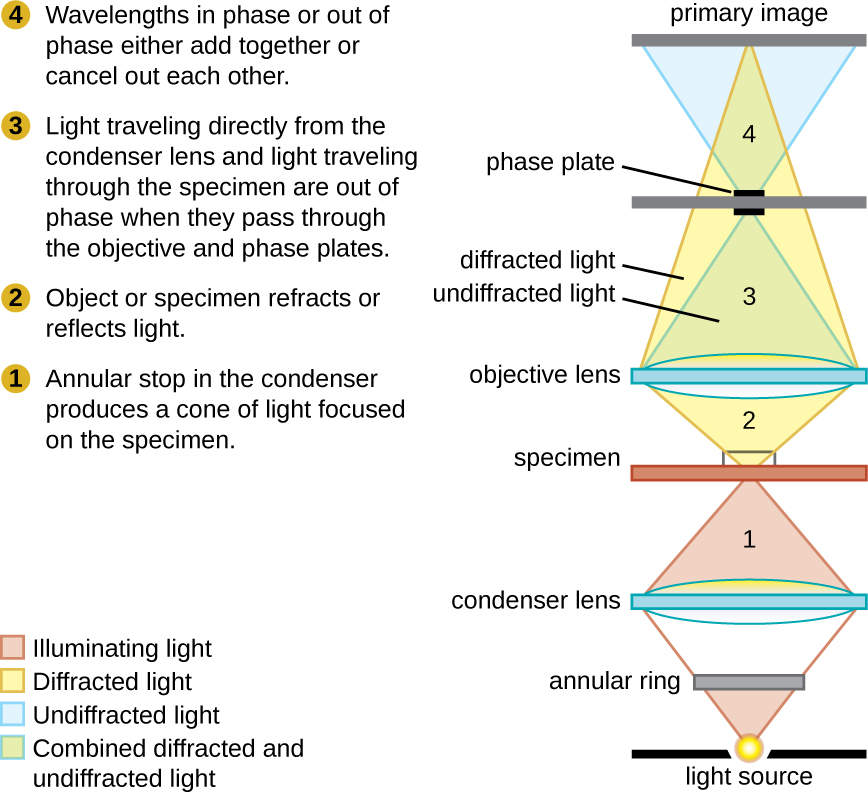
Phase-contrast microscopes use refraction and interference caused by structures in a specimen to create high-contrast, high-resolution images without staining. It is the oldest and simplest type of microscope that creates an image by altering the wavelengths of light rays passing through the specimen. To create altered wavelength paths, an annular stop is used in the condenser. The annular stop produces a hollow cone of light that is focused on the specimen before reaching the objective lens. The objective contains a phase plate containing a phase ring. As a result, light traveling directly from the illuminator passes through the phase ring while light refracted or reflected by the specimen passes through the plate. This causes waves traveling through the ring to be about one-half of a wavelength out of phase with those passing through the plate. Because waves have peaks and troughs, they can add together (if in phase together) or cancel each other out (if out of phase). When the wavelengths are out of phase, wave troughs will cancel out wave peaks, which is called destructive interference. Structures that refract light then appear dark against a bright background of only unrefracted light. More generally, structures that differ in features such as refractive index will differ in levels of darkness ( [link] ).
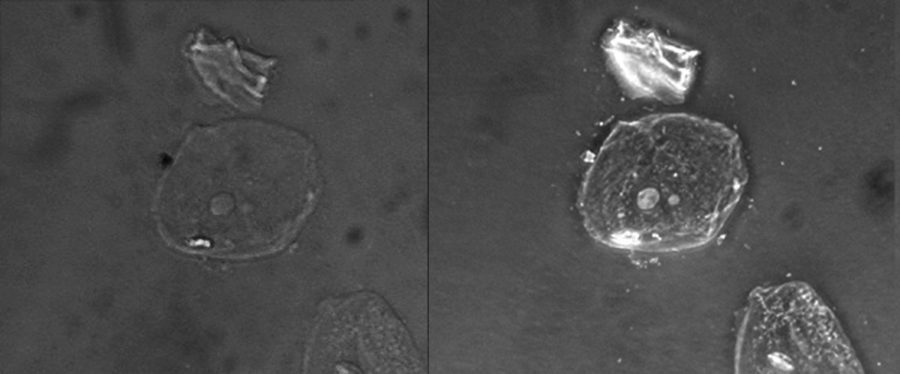
Because it increases contrast without requiring stains, phase-contrast microscopy is often used to observe live specimens. Certain structures, such as organelles in eukaryotic cells and endospores in prokaryotic cells, are especially well visualized with phase-contrast microscopy ( [link] ).
Differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopes (also known as Nomarski optics) are similar to phase-contrast microscopes in that they use interference patterns to enhance contrast between different features of a specimen. In a DIC microscope, two beams of light are created in which the direction of wave movement (polarization) differs. Once the beams pass through either the specimen or specimen-free space, they are recombined and effects of the specimens cause differences in the interference patterns generated by the combining of the beams. This results in high-contrast images of living organisms with a three-dimensional appearance. These microscopes are especially useful in distinguishing structures within live, unstained specimens. ( [link] )

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?