| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Government budget balances can affect the trade balance. As The Keynesian Perspective chapter discusses, a net inflow of foreign financial investment always accompanies a trade deficit, while a net outflow of financial investment always accompanies a trade surplus. One way to understand the connection from budget deficits to trade deficits is that when government creates a budget deficit with some combination of tax cuts or spending increases, it will increase aggregate demand in the economy, and some of that increase in aggregate demand will result in a higher level of imports. A higher level of imports, with exports remaining fixed, will cause a larger trade deficit. That means foreigners’ holdings of dollars increase as Americans purchase more imported goods. Foreigners use those dollars to invest in the United States, which leads to an inflow of foreign investment. One possible source of funding our budget deficit is foreigners buying Treasury securities that are sold by the U.S. government. So a budget deficit is often accompanied by a trade deficit.
In the mid-1980s, it was common to hear economists and even newspaper articles refer to the twin deficits, as the budget deficit and trade deficit both grew substantially. [link] shows the pattern. The federal budget deficit went from 2.6% of GDP in 1981 to 5.1% of GDP in 1985—a drop of 2.5% of GDP. Over that time, the trade deficit moved from 0.5% in 1981 to 2.9% in 1985—a drop of 2.4% of GDP. In the mid-1980s, the considerable increase in government borrowing was matched by an inflow of foreign investment capital, so the government budget deficit and the trade deficit moved together.
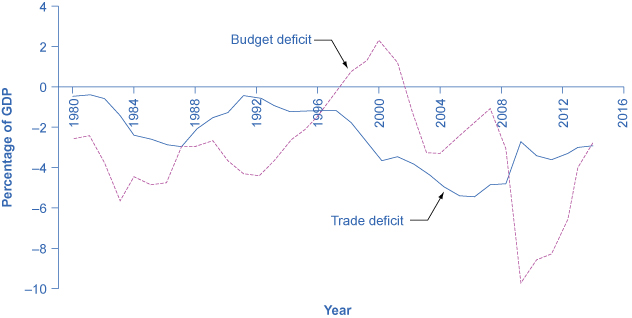
Of course, no one should expect the budget deficit and trade deficit to move in lockstep, because the other parts of the national saving and investment identity—investment and private savings—will often change as well. In the late 1990s, for example, the government budget balance turned from deficit to surplus, but the trade deficit remained large and growing. During this time, the inflow of foreign financial investment was supporting a surge of physical capital investment by U.S. firms. In the first half of the 2000s, the budget and trade deficits again increased together, but in 2009, the budget deficit increased while the trade deficit declined. The budget deficit and the trade deficits are related to each other, but they are more like cousins than twins.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Macroeconomics' conversation and receive update notifications?