| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
In the early 1960s, many leading economists believed that the problem of the business cycle, and the swings between cyclical unemployment and inflation, were a thing of the past. On the cover of its December 31, 1965, issue, Time magazine, then the premier news magazine in the United States, ran a picture of John Maynard Keynes , and the story inside identified Keynesian theories as “the prime influence on the world’s economies.” The article reported that policymakers have “used Keynesian principles not only to avoid the violent [business] cycles of prewar days but to produce phenomenal economic growth and to achieve remarkably stable prices.”
This happy consensus, however, did not last. The U.S. economy suffered one recession from December 1969 to November 1970, a deeper recession from November 1973 to March 1975, and then double-dip recessions from January to June 1980 and from July 1981 to November 1982. At various times, inflation and unemployment both soared. Clearly, the problems of macroeconomic policy had not been completely solved. As economists began to consider what had gone wrong, they identified a number of issues that make discretionary fiscal policy more difficult than it had seemed in the rosy optimism of the mid-1960s.
Because fiscal policy affects the quantity that the government borrows in financial capital markets , it not only affects aggregate demand—it can also affect interest rates. In [link] , the original equilibrium (E 0 ) in the financial capital market occurs at a quantity of $800 billion and an interest rate of 6%. However, an increase in government budget deficits shifts the demand for financial capital from D 0 to D 1 . The new equilibrium (E 1 ) occurs at a quantity of $900 billion and an interest rate of 7%.
A consensus estimate based on a number of studies is that an increase in budget deficits (or a fall in budget surplus) by 1% of GDP will cause an increase of 0.5–1.0% in the long-term interest rate.
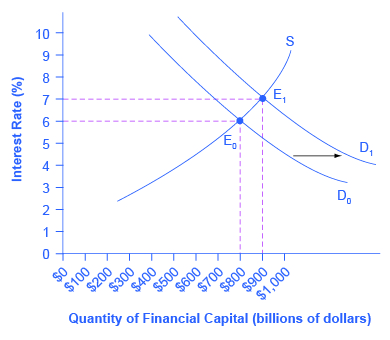
A problem arises here. An expansionary fiscal policy, with tax cuts or spending increases, is intended to increase aggregate demand. If an expansionary fiscal policy also causes higher interest rates, then firms and households are discouraged from borrowing and spending (as occurs with tight monetary policy), thus reducing aggregate demand. Even if the direct effect of expansionary fiscal policy on increasing demand is not totally offset by lower aggregate demand from higher interest rates, fiscal policy can end up being less powerful than was originally expected. This is referred to as crowding out , where government borrowing and spending results in higher interest rates, which reduces business investment and household consumption.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Macroeconomics' conversation and receive update notifications?