| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Most true monopolies today in the U.S. are regulated, natural monopolies. A natural monopoly poses a difficult challenge for competition policy, because the structure of costs and demand seems to make competition unlikely or costly. A natural monopoly arises when average costs are declining over the range of production that satisfies market demand. This typically happens when fixed costs are large relative to variable costs. As a result, one firm is able to supply the total quantity demanded in the market at lower cost than two or more firms—so splitting up the natural monopoly would raise the average cost of production and force customers to pay more.
Public utilities, the companies that have traditionally provided water and electrical service across much of the United States, are leading examples of natural monopoly. It would make little sense to argue that a local water company should be broken up into several competing companies, each with its own separate set of pipes and water supplies. Installing four or five identical sets of pipes under a city, one for each water company, so that each household could choose its own water provider, would be terribly costly. The same argument applies to the idea of having many competing companies for delivering electricity to homes, each with its own set of wires. Before the advent of wireless phones, the argument also applied to the idea of many different phone companies, each with its own set of phone wires running through the neighborhood.
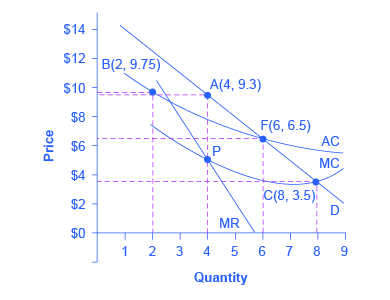
So what then is the appropriate competition policy for a natural monopoly? [link] illustrates the case of natural monopoly, with a market demand curve that cuts through the downward-sloping portion of the average cost curve . Points A, B, C, and F illustrate four of the main choices for regulation. [link] outlines the regulatory choices for dealing with a natural monopoly.
| Quantity | Price | Total Revenue * | Marginal Revenue | Total Cost | Marginal Cost | Average Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 14.7 | 14.7 | - | 11.0 | - | 11.00 |
| 2 | 12.4 | 24.7 | 10.0 | 19.5 | 8.5 | 9.75 |
| 3 | 10.6 | 31.7 | 7.0 | 25.5 | 6.0 | 8.50 |
| 4 | 9.3 | 37.2 | 5.5 | 31.0 | 5.5 | 7.75 |
| 5 | 8.0 | 40.0 | 2.8 | 35.0 | 4.0 | 7.00 |
| 6 | 6.5 | 39.0 | –1.0 | 39.0 | 4.0 | 6.50 |
| 7 | 5.0 | 35.0 | –4.0 | 42.0 | 3.0 | 6.00 |
| 8 | 3.5 | 28.0 | –7.0 | 45.5 | 3.5 | 5.70 |
| 9 | 2.0 | 18.0 | –10.0 | 49.5 | 4.0 | 5.5 |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?