| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
***SORRY, THIS MEDIA TYPE IS NOT SUPPORTED.***
Hình 2.3. Mối quan hệ giữa cấu trúc của cơ thịt cá tuyết và pH
Dấu chấm đen tương ứng với cá đánh bắt ở St. Kilda, biển Đại Tây Dương.
Dấu tam giác tương ứng với cá đánh bắt ở Fyllas Bank, Davis Strait .
Nguồn: Love (1975)
Sự biến đổi pH của cá sau khi chết phụ thuộc rất lớn vào nhiệt độ môi trường
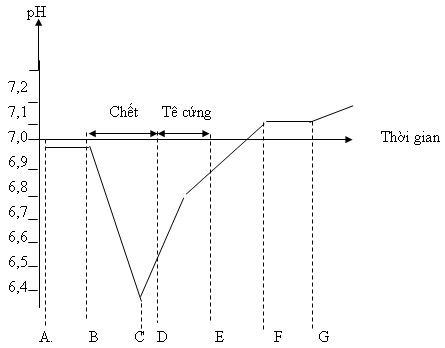
Vd. Ở 5oC, sự biến đổi pH của cá diễn ra như sau (hình 2.4):
A - B: 4 - 6 giờ
B - C - D: 5 - 10 giờ
D - E: 3 - 4 ngày
E - F - G: 3 - 4 ngày
Từ đồ thị hình 2.4 ta thấy khi pH giảm xuống thấp nhất thì cá cứng và khi pH trở lại trung tính thì cá mềm và sau khi mềm thì tiến đến tự phân giải rồi thối rữa.
Khi pH giảm, sự hút nước của cơ thể cá cũng giảm. Khi pH = 7 lượng nước hút vào bằng dung tích của cơ thịt. Khi pH = 6 thì dưới 50% và khi pH = 5 thì gần đến điểm đẳng điện của protein nên lượng nước hút vào bé nhất chỉ khoảng 25%.
Tóm lại: Cá bắt lên một thời gian rồi chết có pH = 7, sau đó giảm xuống đến pH thấp nhất, cá trở nên cứng. pH giảm đến một mức độ nào đó lại tăng lên gần trung tính, cá lúc này trở nên mềm.
Hình 2.4. Sơ đồ sự biến đổi pH của cá sau khi chết
A. Thời gian khi đánh bắtB. Thời gian khi chết, bắt đầu tê cứng
C. Cá có pH thấp nhấtD. Cá cứng nhất
E. Cá bắt đầu mềmF: Cá bắt đầu ươn hỏng
G: Cá ươn hỏng
Sau khi chết, ATP bị phân hủy nhanh tạo thành inosine monophosphate (IMP) bởi enzym nội bào (sự tự phân). Tiếp theo sự phân giải của IMP tạo thành inosine và hypoxanthine là chậm hơn nhiều và được xúc tác chính bởi enzym nội bào IMP phosphohydrolase và inosine ribohydrolase, cùng với sự tham gia của enzym có trong vi khuẩn khi thời gian bảo quản tăng. Sự phân giải ATP được tìm thấy song song với sự mất độ tươi của cá, được xác định bằng phân tích cảm quan.
ATP bị phân hủy xảy ra theo bởi các phản ứng tự phân:
Trong tất cả các loài cá, các giai đoạn tự phân xảy ra giống nhau nhưng tốc độ tự phân khác nhau, thay đổi tùy theo loài.
Glycogen và ATP hầu như biến mất trước giai đoạn tê cứng, trong khi đó IMP và HxR vẫn còn duy trì. Khi hàm lượng IMP và HxR bắt đầu giảm, hàm lượng Hx tăng lên. pH giảm xuống đến mức thấp nhất ở giai đoạn tự phân này.
ATP như là chất chỉ thị hóa học về độ tươi: Chỉ số hóa học về độ tươi của cá là biểu hiện bên ngoài bằng cách định lượng, đánh giá khách quan và cũng có thể bằng cách kiểm tra tự động. Một mình ATP không thể sử dụng để đánh giá độ tươi bởi vì ATP nhanh chóng chuyển đổi tạo thành IMP. Sản phẩm trung gian của sự phân hủy này tăng và giảm làm cho kết quả không chính xác. Khi xác định kết quả, cần chú ý đến inosine và hypoxanthin, chất chuyển hóa cuối cùng của ATP.
Hypoxanthine được dùng như một tiêu chuẩn để đánh giá mức độ tươi của cá. Tuy nhiên, điều này có thể dẫn đến sự nhầm lẫn khi so sánh giữa các loài với nhau. Ở một số loài quá trình phân hủy tạo thành HxR trong khi các loài khác lại sinh Hx. Vì vậy, để nhận biết mức độ tươi của cá một cách chính xác người ta đưa ra trị số K. Trị số K biểu diễn mối liên hệ giữa inosine, hypoxanthine và tổng hàm lượng của ATP thành phần:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chế biến thủy sản' conversation and receive update notifications?