| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
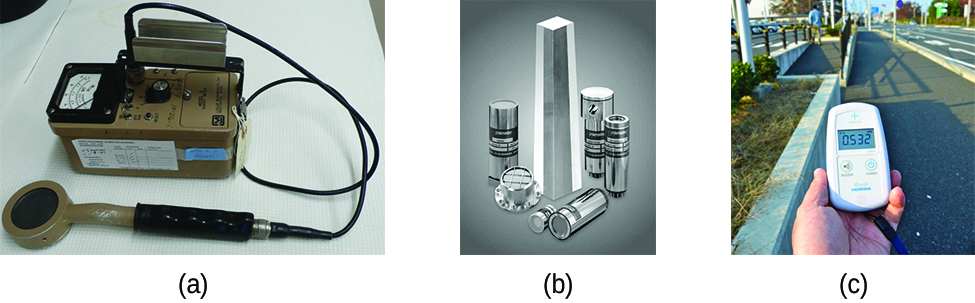
Several different devices are used to detect and measure radiation, including Geiger counters, scintillation counters (scintillators), and radiation dosimeters ( [link] ). Probably the best-known radiation instrument, the Geiger counter (also called the Geiger-Müller counter) detects and measures radiation. Radiation causes the ionization of the gas in a Geiger-Müller tube. The rate of ionization is proportional to the amount of radiation. A scintillation counter contains a scintillator—a material that emits light (luminesces) when excited by ionizing radiation—and a sensor that converts the light into an electric signal. Radiation dosimeters also measure ionizing radiation and are often used to determine personal radiation exposure. Commonly used types are electronic, film badge, thermoluminescent, and quartz fiber dosimeters.
A variety of units are used to measure various aspects of radiation ( [link] ). The SI unit for rate of radioactive decay is the becquerel (Bq) , with 1 Bq = 1 disintegration per second. The curie (Ci) and millicurie (mCi) are much larger units and are frequently used in medicine (1 curie = 1 Ci = 3.7 10 10 disintegrations per second). The SI unit for measuring radiation dose is the gray (Gy) , with 1 Gy = 1 J of energy absorbed per kilogram of tissue. In medical applications, the radiation absorbed dose (rad) is more often used (1 rad = 0.01 Gy; 1 rad results in the absorption of 0.01 J/kg of tissue). The SI unit measuring tissue damage caused by radiation is the sievert (Sv) . This takes into account both the energy and the biological effects of the type of radiation involved in the radiation dose. The roentgen equivalent for man (rem) is the unit for radiation damage that is used most frequently in medicine (1 rem = 1 Sv). Note that the tissue damage units (rem or Sv) includes the energy of the radiation dose (rad or Gy) along with a biological factor referred to as the RBE (for relative biological effectiveness ) that is an approximate measure of the relative damage done by the radiation. These are related by:
with RBE approximately 10 for α radiation, 2(+) for protons and neutrons, and 1 for β and γ radiation.
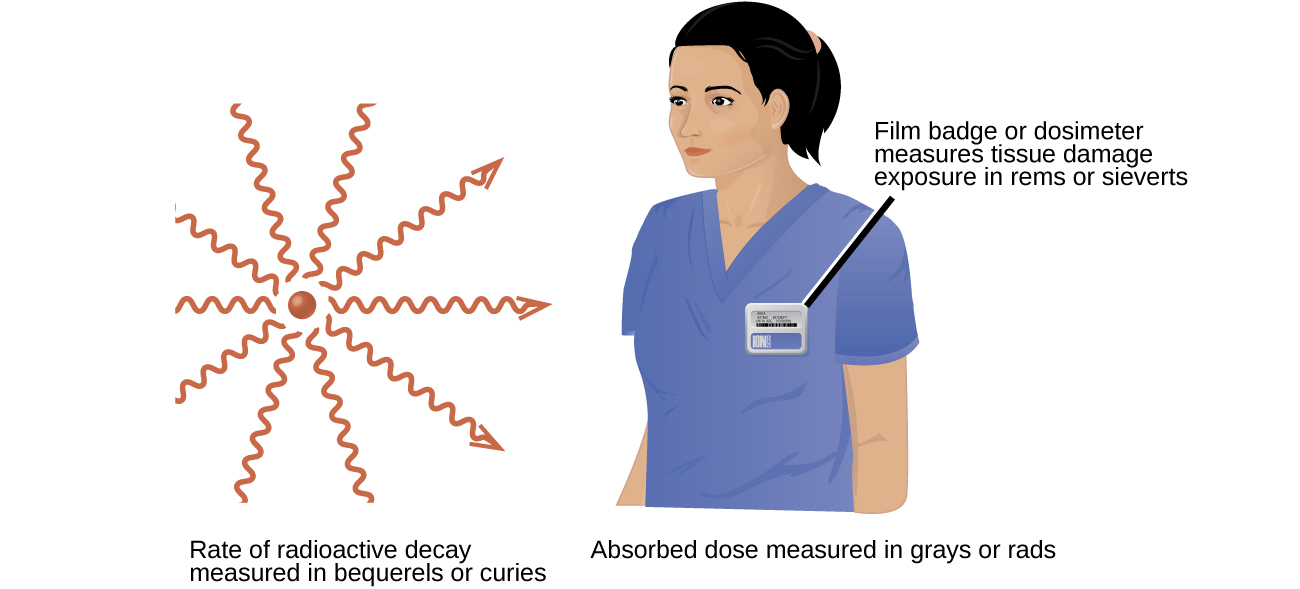
[link] summarizes the units used for measuring radiation.
| Units Used for Measuring Radiation | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement Purpose | Unit | Quantity Measured | Description |
| activity of source | becquerel (Bq) | radioactive decays or emissions | amount of sample that undergoes 1 decay/second |
| curie (Ci) | amount of sample that undergoes 3.7 10 10 decays/second | ||
| absorbed dose | gray (Gy) | energy absorbed per kg of tissue | 1 Gy = 1 J/kg tissue |
| radiation absorbed dose (rad) | 1 rad = 0.01 J/kg tissue | ||
| biologically effective dose | sievert (Sv) | tissue damage | Sv = RBE Gy |
| roentgen equivalent for man (rem) | Rem = RBE rad |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?