| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Over 90% of naturally occurring and man-made solids are crystalline. Most solids form with a regular arrangement of their particles because the overall attractive interactions between particles are maximized, and the total intermolecular energy is minimized, when the particles pack in the most efficient manner. The regular arrangement at an atomic level is often reflected at a macroscopic level. In this module, we will explore some of the details about the structures of metallic and ionic crystalline solids, and learn how these structures are determined experimentally.
We will begin our discussion of crystalline solids by considering elemental metals, which are relatively simple because each contains only one type of atom. A pure metal is a crystalline solid with metal atoms packed closely together in a repeating pattern. Some of the properties of metals in general, such as their malleability and ductility, are largely due to having identical atoms arranged in a regular pattern. The different properties of one metal compared to another partially depend on the sizes of their atoms and the specifics of their spatial arrangements. We will explore the similarities and differences of four of the most common metal crystal geometries in the sections that follow.
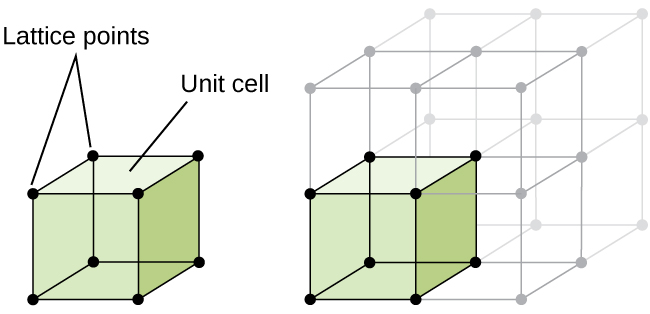
The structure of a crystalline solid, whether a metal or not, is best described by considering its simplest repeating unit, which is referred to as its unit cell . The unit cell consists of lattice points that represent the locations of atoms or ions. The entire structure then consists of this unit cell repeating in three dimensions, as illustrated in [link] .
Let us begin our investigation of crystal lattice structure and unit cells with the most straightforward structure and the most basic unit cell. To visualize this, imagine taking a large number of identical spheres, such as tennis balls, and arranging them uniformly in a container. The simplest way to do this would be to make layers in which the spheres in one layer are directly above those in the layer below, as illustrated in [link] . This arrangement is called simple cubic structure , and the unit cell is called the simple cubic unit cell or primitive cubic unit cell.
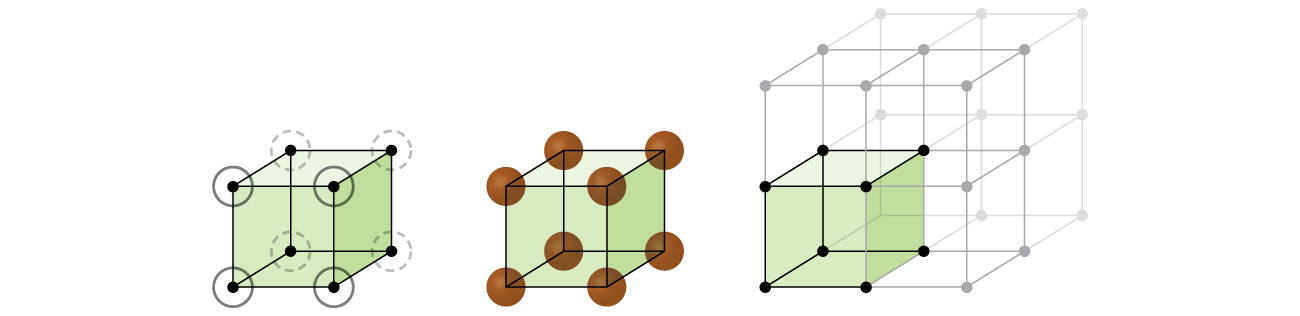
In a simple cubic structure, the spheres are not packed as closely as they could be, and they only “fill” about 52% of the volume of the container. This is a relatively inefficient arrangement, and only one metal (polonium, Po) crystallizes in a simple cubic structure. As shown in [link] , a solid with this type of arrangement consists of planes (or layers) in which each atom contacts only the four nearest neighbors in its layer; one atom directly above it in the layer above; and one atom directly below it in the layer below. The number of other particles that each particle in a crystalline solid contacts is known as its coordination number . For a polonium atom in a simple cubic array, the coordination number is, therefore, six.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?