| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Following the somewhat serendipitous discovery of radioactivity by Becquerel, many prominent scientists began to investigate this new, intriguing phenomenon. Among them were Marie Curie (the first woman to win a Nobel Prize, and the only person to win two Nobel Prizes in different sciences—chemistry and physics), who was the first to coin the term “radioactivity,” and Ernest Rutherford (of gold foil experiment fame), who investigated and named three of the most common types of radiation. During the beginning of the twentieth century, many radioactive substances were discovered, the properties of radiation were investigated and quantified, and a solid understanding of radiation and nuclear decay was developed.
The spontaneous change of an unstable nuclide into another is radioactive decay . The unstable nuclide is called the parent nuclide ; the nuclide that results from the decay is known as the daughter nuclide . The daughter nuclide may be stable, or it may decay itself. The radiation produced during radioactive decay is such that the daughter nuclide lies closer to the band of stability than the parent nuclide, so the location of a nuclide relative to the band of stability can serve as a guide to the kind of decay it will undergo ( [link] ).
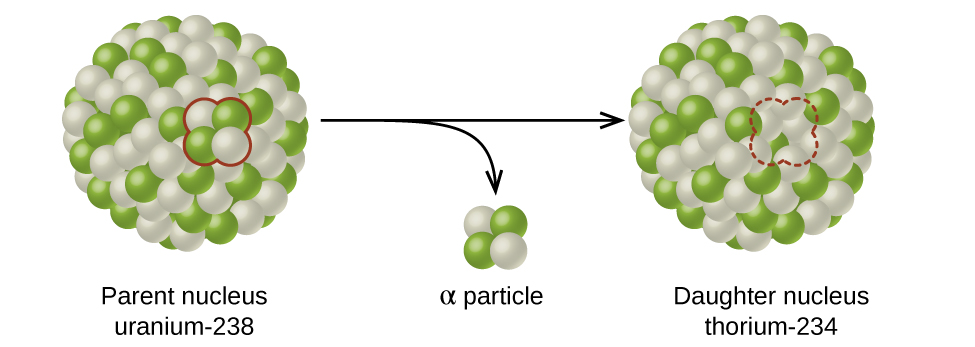
Although the radioactive decay of a nucleus is too small to see with the naked eye, we can indirectly view radioactive decay in an environment called a cloud chamber. Click here to learn about cloud chambers and to view an interesting Cloud Chamber Demonstration from the Jefferson Lab.
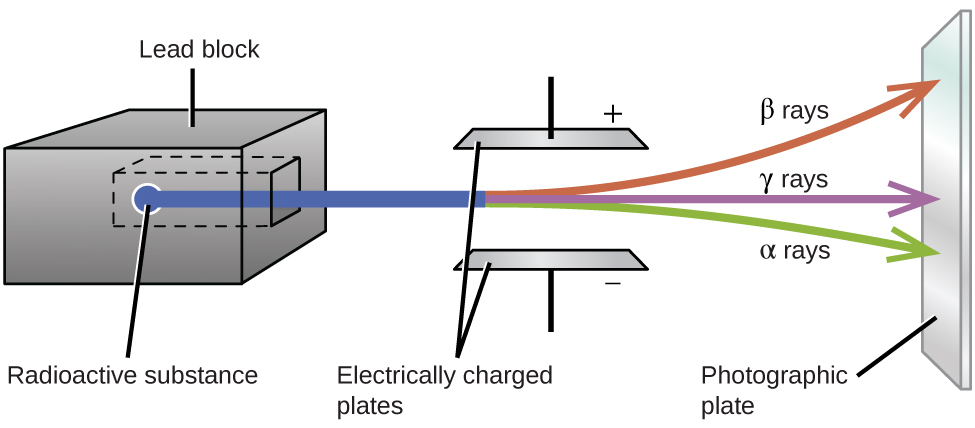
Ernest Rutherford’s experiments involving the interaction of radiation with a magnetic or electric field ( [link] ) helped him determine that one type of radiation consisted of positively charged and relatively massive α particles; a second type was made up of negatively charged and much less massive β particles; and a third was uncharged electromagnetic waves, γ rays. We now know that α particles are high-energy helium nuclei, β particles are high-energy electrons, and γ radiation compose high-energy electromagnetic radiation. We classify different types of radioactive decay by the radiation produced.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?