| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The SI base unit of time is the second (s) . Small and large time intervals can be expressed with the appropriate prefixes; for example, 3 microseconds = 0.000003 s = 3 10 −6 and 5 megaseconds = 5,000,000 s = 5 10 6 s. Alternatively, hours, days, and years can be used.
We can derive many units from the seven SI base units. For example, we can use the base unit of length to define a unit of volume, and the base units of mass and length to define a unit of density.
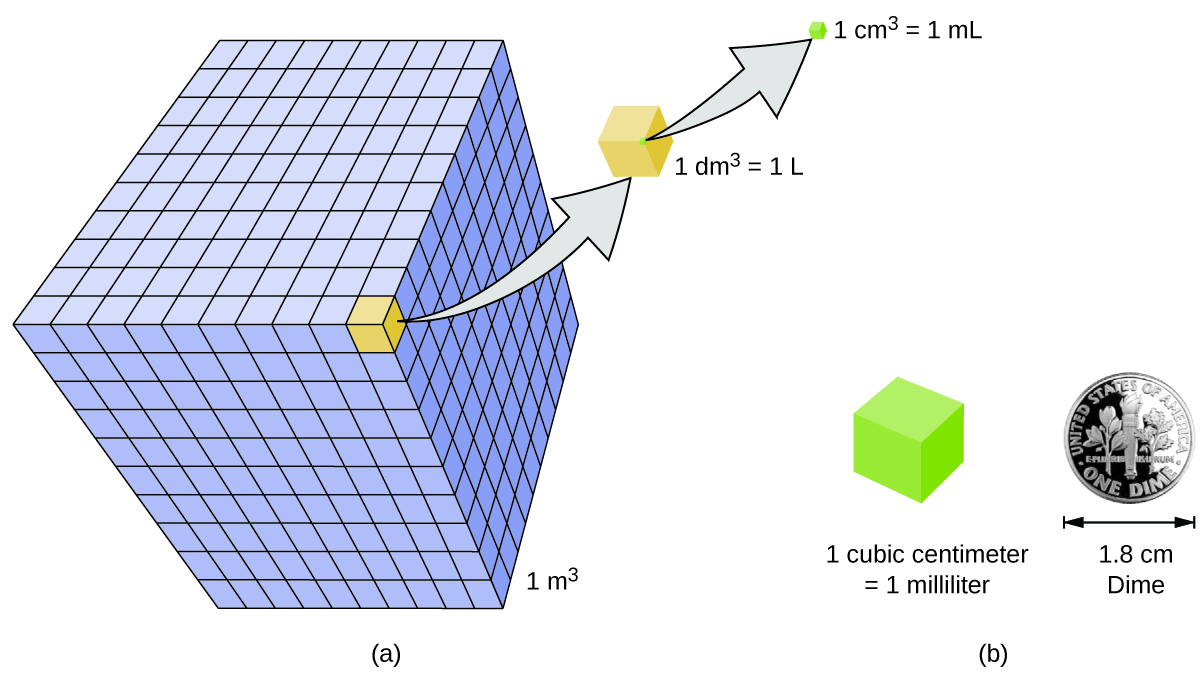
Volume is the measure of the amount of space occupied by an object. The standard SI unit of volume is defined by the base unit of length ( [link] ). The standard volume is a cubic meter (m 3 ) , a cube with an edge length of exactly one meter. To dispense a cubic meter of water, we could build a cubic box with edge lengths of exactly one meter. This box would hold a cubic meter of water or any other substance.
A more commonly used unit of volume is derived from the decimeter (0.1 m, or 10 cm). A cube with edge lengths of exactly one decimeter contains a volume of one cubic decimeter (dm 3 ). A liter (L) is the more common name for the cubic decimeter. One liter is about 1.06 quarts.
A cubic centimeter (cm 3 ) is the volume of a cube with an edge length of exactly one centimeter. The abbreviation cc (for c ubic c entimeter) is often used by health professionals. A cubic centimeter is also called a milliliter (mL) and is 1/1000 of a liter.
We use the mass and volume of a substance to determine its density. Thus, the units of density are defined by the base units of mass and length.
The density of a substance is the ratio of the mass of a sample of the substance to its volume. The SI unit for density is the kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m 3 ). For many situations, however, this as an inconvenient unit, and we often use grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm 3 ) for the densities of solids and liquids, and grams per liter (g/L) for gases. Although there are exceptions, most liquids and solids have densities that range from about 0.7 g/cm 3 (the density of gasoline) to 19 g/cm 3 (the density of gold). The density of air is about 1.2 g/L. [link] shows the densities of some common substances.
| Densities of Common Substances | ||
|---|---|---|
| Solids | Liquids | Gases (at 25 °C and 1 atm) |
| ice (at 0 °C) 0.92 g/cm 3 | water 1.0 g/cm 3 | dry air 1.20 g/L |
| oak (wood) 0.60–0.90 g/cm 3 | ethanol 0.79 g/cm 3 | oxygen 1.31 g/L |
| iron 7.9 g/cm 3 | acetone 0.79 g/cm 3 | nitrogen 1.14 g/L |
| copper 9.0 g/cm 3 | glycerin 1.26 g/cm 3 | carbon dioxide 1.80 g/L |
| lead 11.3 g/cm 3 | olive oil 0.92 g/cm 3 | helium 0.16 g/L |
| silver 10.5 g/cm 3 | gasoline 0.70–0.77 g/cm 3 | neon 0.83 g/L |
| gold 19.3 g/cm 3 | mercury 13.6 g/cm 3 | radon 9.1 g/L |
While there are many ways to determine the density of an object, perhaps the most straightforward method involves separately finding the mass and volume of the object, and then dividing the mass of the sample by its volume. In the following example, the mass is found directly by weighing, but the volume is found indirectly through length measurements.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?