| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
(a) Na 2 [PtCl 6 ]
(b) K 3 [Fe(C 2 O 4 ) 3 ]
(c) [Co(NH 3 ) 5 Cl]Cl 2
K[Ag(CN) 2 ]; coordination number two
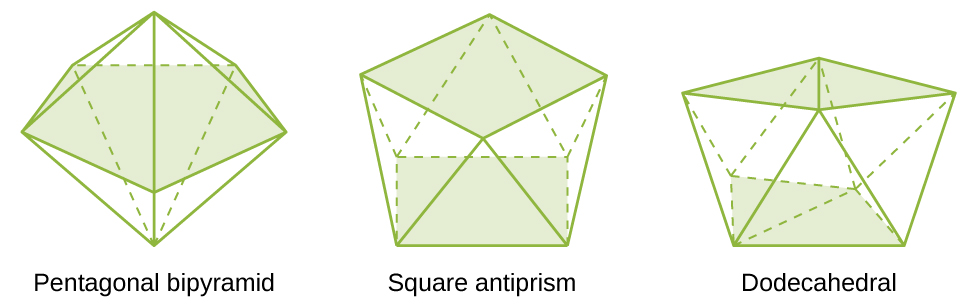
The most common structures of the complexes in coordination compounds are octahedral, tetrahedral, and square planar (see [link] ). For transition metal complexes, the coordination number determines the geometry around the central metal ion. [link] compares coordination numbers to the molecular geometry:
| Coordination Numbers and Molecular Geometry | ||
|---|---|---|
| Coordination Number | Molecular Geometry | Example |
| 2 | linear | [Ag(NH 3 ) 2 ] + |
| 3 | trigonal planar | [Cu(CN) 3 ] 2− |
| 4 | tetrahedral( d 0 or d 10 ), low oxidation states for M | [Ni(CO) 4 ] |
| 4 | square planar ( d 8 ) | [NiCl 4 ] 2− |
| 5 | trigonal bipyramidal | [CoCl 5 ] 2− |
| 5 | square pyramidal | [VO(CN) 4 ] 2− |
| 6 | octahedral | [CoCl 6 ] 3− |
| 7 | pentagonal bipyramid | [ZrF 7 ] 3− |
| 8 | square antiprism | [ReF 8 ] 2− |
| 8 | dodecahedron | [Mo(CN) 8 ] 4− |
| 9 and above | more complicated structures | [ReH 9 ] 2− |
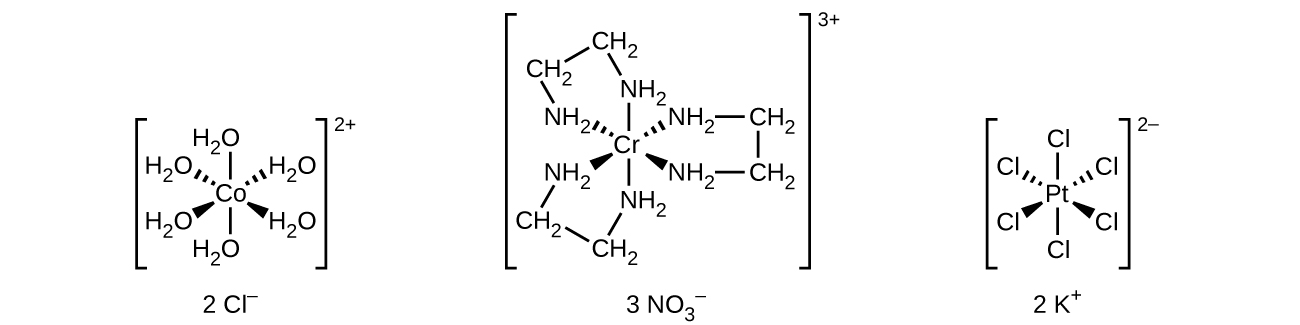
Unlike main group atoms in which both the bonding and nonbonding electrons determine the molecular shape, the nonbonding d -electrons do not change the arrangement of the ligands. Octahedral complexes have a coordination number of six, and the six donor atoms are arranged at the corners of an octahedron around the central metal ion. Examples are shown in [link] . The chloride and nitrate anions in [Co(H 2 O) 6 ]Cl 2 and [Cr(en) 3 ](NO 3 ) 3 , and the potassium cations in K 2 [PtCl 6 ], are outside the brackets and are not bonded to the metal ion.
For transition metals with a coordination number of four, two different geometries are possible: tetrahedral or square planar. Unlike main group elements, where these geometries can be predicted from VSEPR theory, a more detailed discussion of transition metal orbitals (discussed in the section on Crystal Field Theory) is required to predict which complexes will be tetrahedral and which will be square planar. In tetrahedral complexes such as [Zn(CN) 4 ] 2− ( [link] ), each of the ligand pairs forms an angle of 109.5°. In square planar complexes, such as [Pt(NH 3 ) 2 Cl 2 ], each ligand has two other ligands at 90° angles (called the cis positions) and one additional ligand at an 180° angle, in the trans position.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?