| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
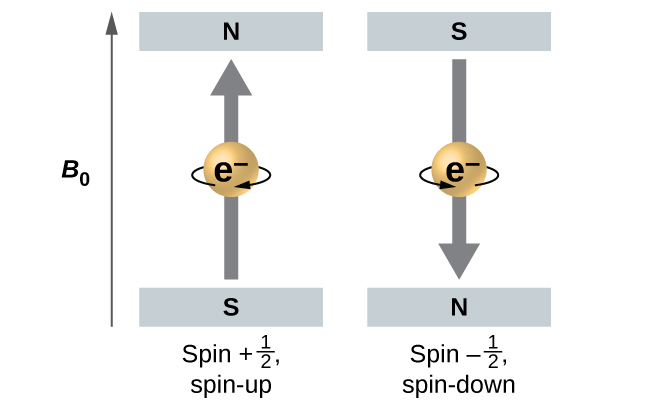
[link] illustrates this phenomenon. An electron acts like a tiny magnet. Its moment is directed up (in the positive direction of the z axis) for the spin quantum number and down (in the negative z direction) for the spin quantum number of A magnet has a lower energy if its magnetic moment is aligned with the external magnetic field (the left electron on [link] ) and a higher energy for the magnetic moment being opposite to the applied field. This is why an electron with has a slightly lower energy in an external field in the positive z direction, and an electron with has a slightly higher energy in the same field. This is true even for an electron occupying the same orbital in an atom. A spectral line corresponding to a transition for electrons from the same orbital but with different spin quantum numbers has two possible values of energy; thus, the line in the spectrum will show a fine structure splitting.
An electron in an atom is completely described by four quantum numbers: n , l , m l , and m s . The first three quantum numbers define the orbital and the fourth quantum number describes the intrinsic electron property called spin. An Austrian physicist Wolfgang Pauli formulated a general principle that gives the last piece of information that we need to understand the general behavior of electrons in atoms. The Pauli exclusion principle can be formulated as follows: No two electrons in the same atom can have exactly the same set of all the four quantum numbers. What this means is that electrons can share the same orbital (the same set of the quantum numbers n , l , and m l ), but only if their spin quantum numbers m s have different values. Since the spin quantum number can only have two values no more than two electrons can occupy the same orbital (and if two electrons are located in the same orbital, they must have opposite spins). Therefore, any atomic orbital can be populated by only zero, one, or two electrons.
The properties and meaning of the quantum numbers of electrons in atoms are briefly summarized in [link] .
| Quantum Numbers, Their Properties, and Significance | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Symbol | Allowed values | Physical meaning |
| principle quantum number | n | 1, 2, 3, 4, …. | shell, the general region for the value of energy for an electron on the orbital |
| angular momentum or azimuthal quantum number | l | 0 ≤ l ≤ n – 1 | subshell, the shape of the orbital |
| magnetic quantum number | m l | – l ≤ m l ≤ l | orientation of the orbital |
| spin quantum number | m s | direction of the intrinsic quantum “spinning” of the electron |
(a) 3 p (b) 5 f (c) 2 s

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?